Page 521 - Rock Mechanics For Underground Mining
P. 521
DISCONTINUOUS SUBSIDENCE ASSOCIATED WITH CAVING METHODS OF MINING
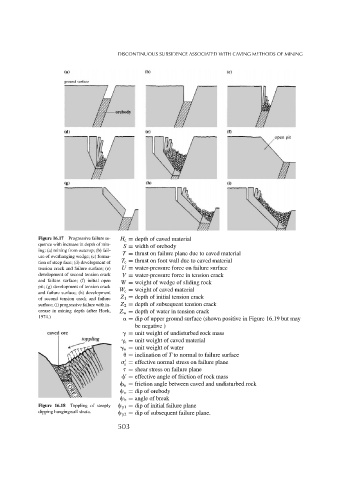
Figure 16.17 Progressive failure se- H c = depth of caved material
quence with increase in depth of min- S = width of orebody
ing: (a) mining from outcrop; (b) fail- T = thrust on failure plane due to caved material
ure of overhanging wedge; (c) forma-
tion of steep face; (d) development of T c = thrust on foot wall due to caved material
tension crack and failure surface; (e) U = water-pressure force on failure surface
development of second tension crack V = water-pressure force in tension crack
and failure surface; (f) initial open
W = weight of wedge of sliding rock
pit; (g) development of tension crack
W c = weight of caved material
and failure surface; (h) development
Z 1 = depth of initial tension crack
of second tension crack and failure
surface; (i) progressive failure with in- Z 2 = depth of subsequent tension crack
crease in mining depth (after Hoek, Z w = depth of water in tension crack
1974.)
= dip of upper ground surface (shown positive in Figure 16.19 but may
be negative )
= unit weight of undisturbed rock mass
c = unit weight of caved material
w = unit weight of water
= inclination of T to normal to failure surface
= effective normal stress on failure plane
n
= shear stress on failure plane
= effective angle of friction of rock mass
w = friction angle between caved and undisturbed rock
o = dip of orebody
b = angle of break
Figure 16.18 Toppling of steeply p1 = dip of initial failure plane
dipping hangingwall strata. p2 = dip of subsequent failure plane.
503