Page 184 - Root Cause Failure Analysis
P. 184
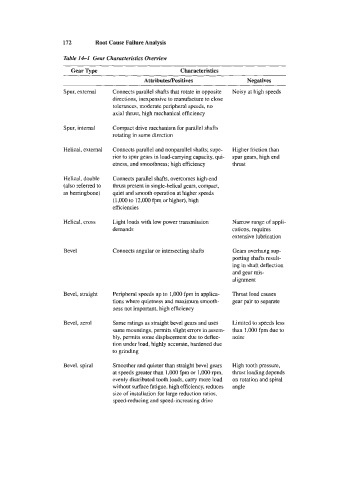
172 Root Cause Failure Analysis
Table 161 Gear Characteristics Overview
Gear Type Characteristics
AttributedPositives Negatives
Spur, external Connects parallel shafts that rotate in opposite Noisy at high speeds
directions, inexpensive to manufacture to close
tolerances, moderate peripheral speeds, no
axial thrust, high mechanical efficiency
Spur, internal Compact drive mechanism for parallel shafts
rotating in same direction
Helical, external Connects parallel and nonparallel shafts; supe- Higher friction than
rior to spur gears in load-carrying capacity, qui- spur gears, high end
etness, and smoothness; high efficiency thrust
Helical, double Connects parallel shafts, overcomes high-end
(also referred to thrust present in single-helical gears, compact,
as herringbone) quiet and smooth operation at higher speeds
(1,OOO to 12,000 fpm or higher), high
efficiencies
Helical, cross Light loads with low power transmission Narrow range of appli-
demands cations, requires
extensive lubrication
Bevel Connects angular or intersecting shafts Gears overhang sup-
porting shafts result-
ing in shaft deflection
and gear mis-
alignment
Bevel, straight Peripheral speeds up to 1,OOO fpm in applica- Thrust load causes
tions where quietness and maximum smooth- gear pair to separate
ness not important, high efficiency
Bevel, zero1 Same ratings as straight bevel gears and uses Limited to speeds less
same mountings, permits slight errors in assem- than 1,000 fpm due to
bly, permits some displacement due to deflec- noise
tion under load, highly accurate, hardened due
to grinding
Bevel, spiral Smoother and quieter than straight bevel gears High tooth pressure,
at speeds greater than 1,000 fpm or 1 ,OOO rpm, thrust loading depends
evenly distributed tooth loads, carry more load on rotation and spiral
without surface fatigue, high efficiency, reduces angle
size of installation for large reduction ratios,
speed-reducing and speed-increasing drive