Page 56 - Root Cause Failure Analysis
P. 56
.
Root Cause Failure Analysis Methodology 47
EVALUATING POTENTIAL CORRECTIVE ACTIONS
The RCFA process defines one or more potential corrective actions that should resolve
the incident or event under investigation. The next step in the analysis is to determine
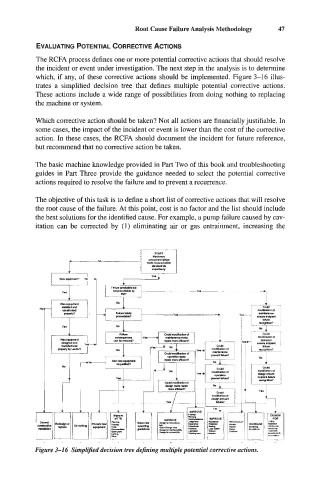
which, if any, of these corrective actions should be implemented. Figure 3-16 illus-
trates a simplified decision tree that defines multiple potential corrective actions.
These actions include a wide range of possibilities from doing nothing to replacing
the machine or system.
Which corrective action should be taken? Not all actions are financially justifiable. In
some cases, the impact of the incident or event is lower than the cost of the corrective
action. In these cases, the RCFA should document the incident for future reference,
but recommend that no corrective action be taken.
The basic machine knowledge provided in Part Two of this book and troubleshooting
guides in Part Three provide the guidance needed to select the potential corrective
actions required to resolve the failure and to prevent a recurrence.
The objective of this task is to define a short list of corrective actions that will resolve
the root cause of the failure. At this point, cost is no factor and the list should include
the best solutions for the identified cause. For example, a pump failure caused by cav-
itation can be corrected by (1) eliminating air or gas entrainment, increasing the
Figure 3-1 6 Simplified decision tree de$ning multiple potential corrective actions.