Page 14 - Rotating Machinery Pratical Solutions to Unbalance and Misalignment
P. 14
Introduction to Vibrations
FREQUENCY
Frequency is the number of complete oscillations completed
in a unit time, or simply expressed as 1/T. Generally it is measured
in either cycles per second or cycles per minute.
In dealing with machine vibrations, it is usually desirable to
express frequency in terms of cycles per minute, since we measure
the rotational speed of machinery in revolutions per minute. This
allows examination of the vibration frequency in terms of mul-
tiples of the rotational speed. The two times rotational speed is
known as the second harmonic, and the three times rotational
speed is the third harmonic.
Rotational speed is also known as the fundamental fre-
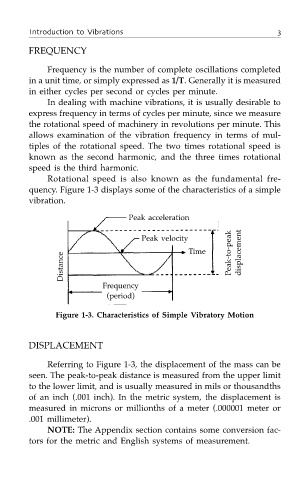
quency. Figure 1-3 displays some of the characteristics of a simple
vibration.
Peak acceleration
Peak velocity Time displacement
Distance Peak-to-peak
Frequency
(period)
Figure 1-3. Characteristics of Simple Vibratory Motion
DISPLACEMENT
Referring to Figure 1-3, the displacement of the mass can be
seen. The peak-to-peak distance is measured from the upper limit
to the lower limit, and is usually measured in mils or thousandths
of an inch (.001 inch). In the metric system, the displacement is
measured in microns or millionths of a meter (.000001 meter or
.001 millimeter).
NOTE: The Appendix section contains some conversion fac-
tors for the metric and English systems of measurement.