Page 129 - Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
P. 129
108 Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
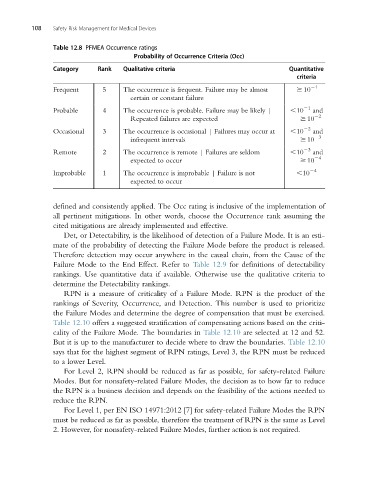
Table 12.8 PFMEA Occurrence ratings
Probability of Occurrence Criteria (Occ)
Category Rank Qualitative criteria Quantitative
criteria
Frequent 5 The occurrence is frequent. Failure may be almost $ 10 21
certain or constant failure
Probable 4 The occurrence is probable. Failure may be likely | ,10 21 and
Repeated failures are expected $ 10 22
Occasional 3 The occurrence is occasional | Failures may occur at ,10 22 and
23
infrequent intervals $ 10
Remote 2 The occurrence is remote | Failures are seldom ,10 23 and
24
expected to occur $ 10
Improbable 1 The occurrence is improbable | Failure is not ,10 24
expected to occur
defined and consistently applied. The Occ rating is inclusive of the implementation of
all pertinent mitigations. In other words, choose the Occurrence rank assuming the
cited mitigations are already implemented and effective.
Det, or Detectability, is the likelihood of detection of a Failure Mode. It is an esti-
mate of the probability of detecting the Failure Mode before the product is released.
Therefore detection may occur anywhere in the causal chain, from the Cause of the
Failure Mode to the End Effect. Refer to Table 12.9 for definitions of detectability
rankings. Use quantitative data if available. Otherwise use the qualitative criteria to
determine the Detectability rankings.
RPN is a measure of criticality of a Failure Mode. RPN is the product of the
rankings of Severity, Occurrence, and Detection. This number is used to prioritize
the Failure Modes and determine the degree of compensation that must be exercised.
Table 12.10 offers a suggested stratification of compensating actions based on the criti-
cality of the Failure Mode. The boundaries in Table 12.10 are selected at 12 and 52.
But it is up to the manufacturer to decide where to draw the boundaries. Table 12.10
says that for the highest segment of RPN ratings, Level 3, the RPN must be reduced
to a lower Level.
For Level 2, RPN should be reduced as far as possible, for safety-related Failure
Modes. But for nonsafety-related Failure Modes, the decision as to how far to reduce
the RPN is a business decision and depends on the feasibility of the actions needed to
reduce the RPN.
For Level 1, per EN ISO 14971:2012 [7] for safety-related Failure Modes the RPN
must be reduced as far as possible, therefore the treatment of RPN is the same as Level
2. However, for nonsafety-related Failure Modes, further action is not required.