Page 151 - Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
P. 151
130 Safety Risk Management for Medical Devices
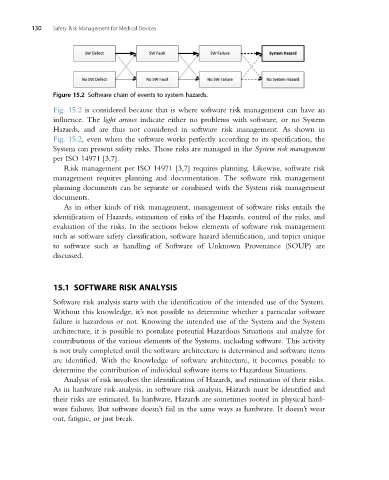
Figure 15.2 Software chain of events to system hazards.
Fig. 15.2 is considered because that is where software risk management can have an
influence. The light arrows indicate either no problems with software, or no System
Hazards, and are thus not considered in software risk management. As shown in
Fig. 15.2, even when the software works perfectly according to its specification, the
System can present safety risks. Those risks are managed in the System risk management
per ISO 14971 [3,7].
Risk management per ISO 14971 [3,7] requires planning. Likewise, software risk
management requires planning and documentation. The software risk management
planning documents can be separate or combined with the System risk management
documents.
As in other kinds of risk management, management of software risks entails the
identification of Hazards, estimation of risks of the Hazards, control of the risks, and
evaluation of the risks. In the sections below elements of software risk management
such as software safety classification, software hazard identification, and topics unique
to software such as handling of Software of Unknown Provenance (SOUP) are
discussed.
15.1 SOFTWARE RISK ANALYSIS
Software risk analysis starts with the identification of the intended use of the System.
Without this knowledge, it’s not possible to determine whether a particular software
failure is hazardous or not. Knowing the intended use of the System and the System
architecture, it is possible to postulate potential Hazardous Situations and analyze for
contributions of the various elements of the Systems, including software. This activity
is not truly completed until the software architecture is determined and software items
are identified. With the knowledge of software architecture, it becomes possible to
determine the contribution of individual software items to Hazardous Situations.
Analysis of risk involves the identification of Hazards, and estimation of their risks.
As in hardware risk-analysis, in software risk-analysis, Hazards must be identified and
their risks are estimated. In hardware, Hazards are sometimes rooted in physical hard-
ware failures. But software doesn’t fail in the same ways as hardware. It doesn’t wear
out, fatigue, or just break.