Page 124 - Satellite Communications, Fourth Edition
P. 124
104 Chapter Four
Free
space
600
500
Approximate heights, km 400
300
200 Ionosphere
100
90
Troposphere
Ice layer rain
Earth’s surface
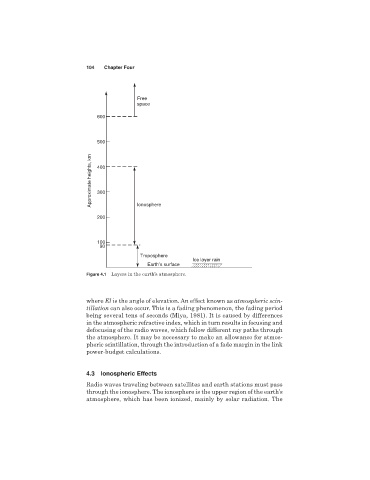
Figure 4.1 Layers in the earth’s atmosphere.
where El is the angle of elevation. An effect known as atmospheric scin-
tillation can also occur. This is a fading phenomenon, the fading period
being several tens of seconds (Miya, 1981). It is caused by differences
in the atmospheric refractive index, which in turn results in focusing and
defocusing of the radio waves, which follow different ray paths through
the atmosphere. It may be necessary to make an allowance for atmos-
pheric scintillation, through the introduction of a fade margin in the link
power-budget calculations.
4.3 Ionospheric Effects
Radio waves traveling between satellites and earth stations must pass
through the ionosphere. The ionosphere is the upper region of the earth’s
atmosphere, which has been ionized, mainly by solar radiation. The