Page 197 - Schaum's Outline of Differential Equations
P. 197
180 NUMERICAL METHODS FOR SOLVING DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS [CHAP. 19
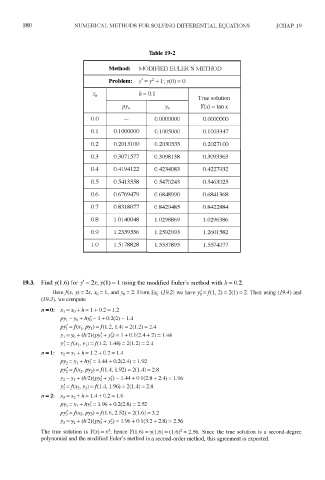
Table 19-2
Method: MODIFIED EULER'S METHOD
2
Problem: / = y + 1 ; y(0) = 0
ft = 0.1
x n
True solution
py n y n Y(x) = tan x
0.0 — 0.0000000 0.0000000
0.1 0.1000000 0.1005000 0.1003347
0.2 0.2015100 0.2030353 0.2027100
0.3 0.3071577 0.3098138 0.3093363
0.4 0.4194122 0.4234083 0.4227932
0.5 0.5413358 0.5470243 0.5463025
0.6 0.6769479 0.6848990 0.6841368
0.7 0.8318077 0.8429485 0.8422884
0.8 1.0140048 1.0298869 1.0296386
0.9 1.2359536 1.2592993 1.2601582
1.0 1.5178828 1.5537895 1.5574077
1
19.3. Find y(l.6) for y = 2x; y(l) = 1 using the modified Euler's method with h = 0.2.
Here/0, y) = 2x,x 0 = 1, and y a = 2. From Eq. (19.2) we have y' Q =/(!, 2) = 2(1) = 2. Then using (19.4) and
(19.3), we compute
2
2
The true solution is Y(x)=x ; hence 7(1.6) = y(l.6) = (1.6) = 2.56. Since the true solution is a second-degree
polynomial and the modified Euler's method is a second-order method, this agreement is expected.