Page 245 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 245
230 EXPANSION OF SOLIDS, LIQUIDS, AND GASES [CHAP. 19
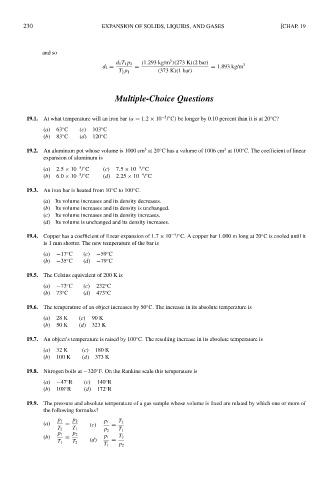
and so
3
d 1 T 1 p 2 (1.293 kg/m )(273 K)(2 bar) 3
d 2 = = = 1.893 kg/m
T 2 p 1 (373 K)(1 bar)
Multiple-Choice Questions
−5 ◦
19.1. At what temperature will an iron bar (a = 1.2 × 10 / C) be longer by 0.10 percent than it is at 20 C?
◦
◦
◦
(a) 63 C (c) 103 C
(b) 83 C (d) 120 C
◦
◦
3
3
◦
19.2. An aluminum pot whose volume is 1000 cm at 20 C has a volume of 1006 cm at 100 C. The coefficient of linear
◦
expansion of aluminum is
(a) 2.5 × 10 / C (c) 7.5 × 10 / C
−5 ◦
−5 ◦
(b) 6.0 × 10 / C (d) 2.25 × 10 / C
−5 ◦
−4 ◦
◦
◦
19.3. An iron bar is heated from 10 Cto100 C.
(a) Its volume increases and its density decreases.
(b) Its volume increases and its density is unchanged.
(c) Its volume increases and its density increases.
(d) Its volume is unchanged and its density increases.
19.4. Copper has a coefficient of linear expansion of 1.7 × 10 / C. A copper bar 1.000 m long at 20 C is cooled until it
−5 ◦
◦
is 1 mm shorter. The new temperature of the bar is
◦
◦
(a) −17 C (c) −59 C
(b) −35 C (d) −79 C
◦
◦
19.5. The Celsius equivalent of 200 K is
(a) −73 C (c) 232 C
◦
◦
(b) 73 C (d) 473 C
◦
◦
◦
19.6. The temperature of an object increases by 50 C. The increase in its absolute temperature is
(a) 28 K (c) 90 K
(b) 50 K (d) 323 K
◦
19.7. An object’s temperature is raised by 100 C. The resulting increase in its absolute temperature is
(a) 32 K (c) 180 K
(b) 100 K (d) 373 K
◦
19.8. Nitrogen boils at −320 F. On the Rankine scale this temperature is
(a) −47 R (c) 140 R
◦
◦
(b) 108 R (d) 172 R
◦
◦
19.9. The pressure and absolute temperature of a gas sample whose volume is fixed are related by which one or more of
the following formulas?
p 1 p 2
(a) = (c) p 1 = T 2
T 2 T 1
p 2 T 1
p 1 p 2
(b) = (d) p 1 T 2
T 1 T 2 =
T 1 p 2