Page 252 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 252
CHAP. 20] KINETIC THEORY OF MATTER 237
The number of molecules in a mole of any substance is Avogadro’s number N, whose value is
23
N = 6.023 × 10 molecules/mol
The number of molecules in a sample of a substance is the number of moles it contains multiplied by N.
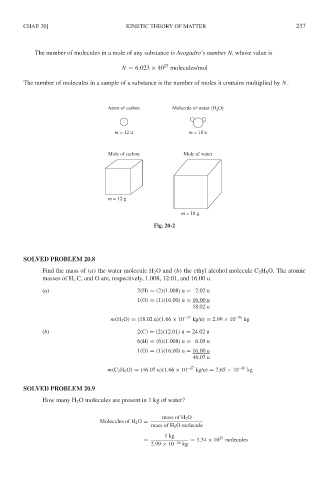
Atom of carbon Molecule of water (H 2 O)
m = 12 u m = 18 u
Mole of carbon Mole of water
m = 12 g
m = 18 g
Fig. 20-2
SOLVED PROBLEM 20.8
Find the mass of (a) the water molecule H 2 O and (b) the ethyl alcohol molecule C 2 H 6 O. The atomic
masses of H, C, and O are, respectively, 1.008, 12.01, and 16.00 u.
(a) 2(H) = (2)(1.008) u = 2.02 u
1(O) = (1)(16.00) u = 16.00 u
18.02 u
m(H 2 O) = (18.02 u)(1.66 × 10 −27 kg/u) = 2.99 × 10 −26 kg
(b) 2(C) = (2)(12.01) u = 24.02 u
6(H) = (6)(1.008) u = 6.05 u
1(O) = (1)(16.00) u = 16.00 u
46.07 u
m(C 2 H 6 O) = (46.07 u)(1.66 × 10 −27 kg/u) = 7.65 × 10 −26 kg
SOLVED PROBLEM 20.9
How many H 2 O molecules are present in 1 kg of water?
mass of H 2 O
Molecules of H 2 O =
mass of H 2 O molecule
1kg 25
= = 3.34 × 10 molecules
2.99 × 10 −26 kg