Page 327 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 327
312 CAPACITANCE [CHAP. 26
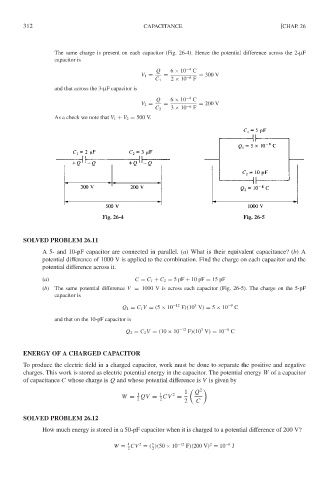
The same charge is present on each capacitor (Fig. 26-4). Hence the potential difference across the 2-µF
capacitor is
Q 6 × 10 −4 C
V 1 = = = 300 V
C 1 2 × 10 −6 F
and that across the 3-µF capacitor is
Q 6 × 10 −4 C
V 2 = = = 200 V
C 2 3 × 10 −6 F
As a check we note that V 1 + V 2 = 500 V.
Fig. 26-4 Fig. 26-5
SOLVED PROBLEM 26.11
A 5- and 10-pF capacitor are connected in parallel. (a) What is their equivalent capacitance? (b)A
potential difference of 1000 V is applied to the combination. Find the charge on each capacitor and the
potential difference across it.
(a) C = C 1 + C 2 = 5pF + 10 pF = 15 pF
(b) The same potential difference V = 1000 V is across each capacitor (Fig. 26-5). The charge on the 5-pF
capacitor is
3
Q 1 = C 1 V = (5 × 10 −12 F)(10 V) = 5 × 10 −9 C
and that on the 10-pF capacitor is
3
Q 2 = C 2 V = (10 × 10 −12 F)(10 V) = 10 −8 C
ENERGY OF A CHARGEDCAPACITOR
To produce the electric field in a charged capacitor, work must be done to separate the positive and negative
charges. This work is stored as electric potential energy in the capacitor. The potential energy W of a capacitor
of capacitance C whose charge is Q and whose potential difference is V is given by
1 Q 2
1 1 2
W = QV = CV =
2 2
2 C
SOLVED PROBLEM 26.12
How much energy is stored in a 50-pF capacitor when it is charged to a potential difference of 200 V?
2
1
1
2
W = CV = ( )(50 × 10 −12 F)(200 V) = 10 −6 J
2 2