Page 389 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 389
374 LIGHT [CHAP. 30
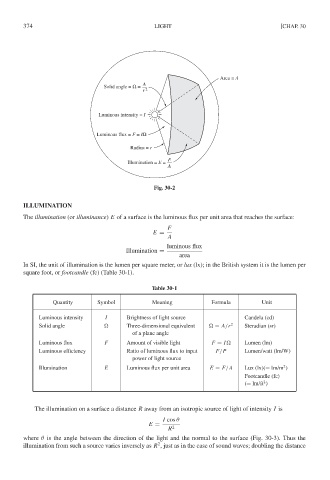
Area = A
A
Solid angle = Ω =
r 2
Luminous intensity = I
Luminous flux = F = IΩ
Radius = r
F
Illumination = E =
A
Fig. 30-2
ILLUMINATION
The illumination (or illuminance) E of a surface is the luminous flux per unit area that reaches the surface:
F
E =
A
luminous flux
Illumination =
area
In SI, the unit of illumination is the lumen per square meter, or lux (lx); in the British system it is the lumen per
square foot, or footcandle (fc) (Table 30-1).
Table 30-1
Quantity Symbol Meaning Formula Unit
Luminous intensity I Brightness of light source Candela (cd)
Solid angle Three-dimensional equivalent = A/r 2 Steradian (sr)
of a plane angle
Luminous flux F Amount of visible light F = I Lumen (lm)
Luminous efficiency Ratio of luminous flux to input F/P Lumen/watt (lm/W)
power of light source
2
Illumination E Luminous flux per unit area E = F/A Lux (lx)(= lm/m )
Footcandle (fc)
2
(= lm/ft )
The illumination on a surface a distance R away from an isotropic source of light of intensity I is
I cos θ
E = 2
R
where θ is the angle between the direction of the light and the normal to the surface (Fig. 30-3). Thus the
2
illumination from such a source varies inversely as R , just as in the case of sound waves; doubling the distance