Page 393 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 393
378 LIGHT [CHAP. 30
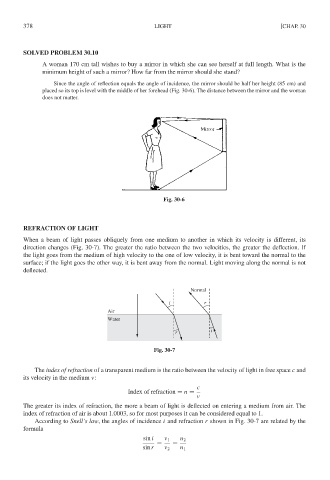
SOLVED PROBLEM 30.10
A woman 170 cm tall wishes to buy a mirror in which she can see herself at full length. What is the
minimum height of such a mirror? How far from the mirror should she stand?
Since the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence, the mirror should be half her height (85 cm) and
placed so its top is level with the middle of her forehead (Fig. 30-6). The distance between the mirror and the woman
does not matter.
Fig. 30-6
REFRACTION OF LIGHT
When a beam of light passes obliquely from one medium to another in which its velocity is different, its
direction changes (Fig. 30-7). The greater the ratio between the two velocities, the greater the deflection. If
the light goes from the medium of high velocity to the one of low velocity, it is bent toward the normal to the
surface; if the light goes the other way, it is bent away from the normal. Light moving along the normal is not
deflected.
Normal
i r
Air
Water
r i
Fig. 30-7
The index of refraction of a transparent medium is the ratio between the velocity of light in free space c and
its velocity in the medium v:
c
Index of refraction = n =
v
The greater its index of refraction, the more a beam of light is deflected on entering a medium from air. The
index of refraction of air is about 1.0003, so for most purposes it can be considered equal to 1.
According to Snell’s law, the angles of incidence i and refraction r shown in Fig. 30-7 are related by the
formula
sin i v 1 n 2
= =
sinr v 2 n 1