Page 418 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 418
CHAP. 32] LENSES 403
The required focal length is therefore
pq (27.8cm)(500 cm)
f = = = 26.3cm = 263 mm
p + q 27.8cm + 500 cm
SOLVED PROBLEM 32.16
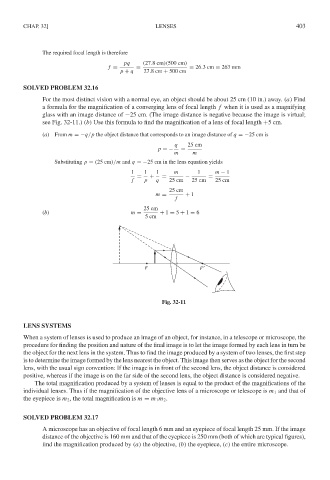
For the most distinct vision with a normal eye, an object should be about 25 cm (10 in.) away. (a) Find
a formula for the magnification of a converging lens of focal length f when it is used as a magnifying
glass with an image distance of −25 cm. (The image distance is negative because the image is virtual;
see Fig. 32-11.) (b) Use this formula to find the magnification of a lens of focal length +5 cm.
(a) From m =−q/p the object distance that corresponds to an image distance of q =−25 cm is
q 25 cm
p =− =
m m
Substituting p = (25 cm)/m and q =−25 cm in the lens equation yields
1 1 1 m 1 m − 1
= + = − =
f p q 25 cm 25 cm 25 cm
25 cm
m = + 1
f
25 cm
(b) m = + 1 = 5 + 1 = 6
5cm
F F′
Fig. 32-11
LENS SYSTEMS
When a system of lenses is used to produce an image of an object, for instance, in a telescope or microscope, the
procedure for finding the position and nature of the final image is to let the image formed by each lens in turn be
the object for the next lens in the system. Thus to find the image produced by a system of two lenses, the first step
is to determine the image formed by the lens nearest the object. This image then serves as the object for the second
lens, with the usual sign convention: If the image is in front of the second lens, the object distance is considered
positive, whereas if the image is on the far side of the second lens, the object distance is considered negative.
The total magnification produced by a system of lenses is equal to the product of the magnifications of the
individual lenses. Thus if the magnification of the objective lens of a microscope or telescope is m 1 and that of
the eyepiece is m 2 , the total magnification is m = m 1 m 2 .
SOLVED PROBLEM 32.17
A microscope has an objective of focal length 6 mm and an eyepiece of focal length 25 mm. If the image
distance of the objective is 160 mm and that of the eyepiece is 250 mm (both of which are typical figures),
find the magnification produced by (a) the objective, (b) the eyepiece, (c) the entire microscope.