Page 74 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 74
CHAP. 5] LAWS OF MOTION 59
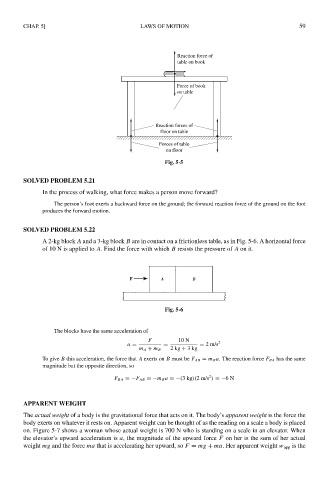
Reaction force of
table on book
Force of book
on table
Reaction forces of
floor on table
Forces of table
on floor
Fig. 5-5
SOLVED PROBLEM 5.21
In the process of walking, what force makes a person move forward?
The person’s foot exerts a backward force on the ground; the forward reaction force of the ground on the foot
produces the forward motion.
SOLVED PROBLEM 5.22
A 2-kg block A and a 3-kg block B are in contact on a frictionless table, as in Fig. 5-6. A horizontal force
of 10 N is applied to A. Find the force with which B resists the pressure of A on it.
Fig. 5-6
The blocks have the same acceleration of
F 10 N
a = = = 2 m/s 2
m A + m B 2kg + 3kg
To give B this acceleration, the force that A exerts on B must be F AB = m B a. The reaction force F BA has the same
magnitude but the opposite direction, so
2
F BA =−F AB =−m B a =−(3kg)(2 m/s ) =−6N
APPARENT WEIGHT
The actual weight of a body is the gravitational force that acts on it. The body’s apparentweight is the force the
body exerts on whatever it rests on. Apparent weight can be thought of as the reading on a scale a body is placed
on. Figure 5-7 shows a woman whose actual weight is 700 N who is standing on a scale in an elevator. When
the elevator’s upward acceleration is a, the magnitude of the upward force F on her is the sum of her actual
weight mg and the force ma that is accelerating her upward, so F = mg + ma. Her apparent weight w app is the