Page 76 - Schaum's Outline of Theory and Problems of Applied Physics
P. 76
CHAP. 5] LAWS OF MOTION 61
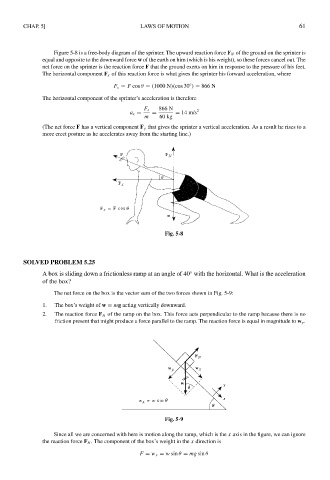
Figure 5-8 is a free-body diagram of the sprinter. The upward reaction force F N of the ground on the sprinter is
equal and opposite to the downward force w of the earth on him (which is his weight), so these forces cancel out. The
net force on the sprinter is the reaction force F that the ground exerts on him in response to the pressure of his feet.
The horizontal component F x of this reaction force is what gives the sprinter his forward acceleration, where
F x = F cos θ = (1000 N)(cos 30 ) = 866 N
◦
The horizontal component of the sprinter’s acceleration is therefore
F x 866 N 2
a x = = = 14 m/s
m 60 kg
(The net force F has a vertical component F y that gives the sprinter a vertical acceleration. As a result he rises to a
more erect posture as he accelerates away from the starting line.)
Fig. 5-8
SOLVED PROBLEM 5.25
A box is sliding down a frictionless ramp at an angle of 40 with the horizontal. What is the acceleration
◦
of the box?
The net force on the box is the vector sum of the two forces shown in Fig. 5-9:
1. The box’s weight of w = mg acting vertically downward.
2. The reaction force F N of the ramp on the box. This force acts perpendicular to the ramp because there is no
friction present that might produce a force parallel to the ramp. The reaction force is equal in magnitude to w y .
Fig. 5-9
Since all we are concerned with here is motion along the ramp, which is the x axis in the figure, we can ignore
the reaction force F N . The component of the box’s weight in the x direction is
F = w x = w sin θ = mg sin θ