Page 99 - Theory and Problems of BEGINNING CHEMISTRY
P. 99
88 INORGANIC NOMENCLATURE [CHAP. 6
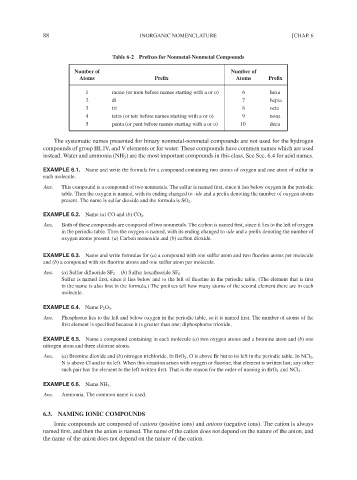
Table 6-2 Prefixes for Nonmetal-Nonmetal Compounds
Number of Number of
Atoms Prefix Atoms Prefix
1 mono (or mon before names starting with a or o) 6 hexa
2 di 7 hepta
3 tri 8 octa
4 tetra (or tetr before names starting with a or o) 9 nona
5 penta (or pent before names starting with a or o) 10 deca
The systematic names presented for binary nonmetal-nonmetal compounds are not used for the hydrogen
compounds of group III, IV, and V elements or for water. These compounds have common names which are used
instead. Water and ammonia (NH 3 ) are the most important compounds in this class. See Sec. 6.4 for acid names.
EXAMPLE 6.1. Name and write the formula for a compound containing two atoms of oxygen and one atom of sulfur in
each molecule.
Ans. This compound is a compound of two nonmetals. The sulfur is named first, since it lies below oxygen in the periodic
table. Then the oxygen is named, with its ending changed to -ide and a prefix denoting the number of oxygen atoms
present. The name is sulfur dioxide and the formula is SO 2 .
EXAMPLE 6.2. Name (a) CO and (b)CO 2 .
Ans. Both of these compounds are composed of two nonmetals. The carbon is named first, since it lies to the left of oxygen
in the periodic table. Then the oxygen is named, with its ending changed to -ide and a prefix denoting the number of
oxygen atoms present. (a) Carbon monoxide and (b) carbon dioxide.
EXAMPLE 6.3. Name and write formulas for (a) a compound with one sulfur atom and two fluorine atoms per molecule
and (b) a compound with six fluorine atoms and one sulfur atom per molecule.
Ans. (a) Sulfur difluoride SF 2 (b) Sulfur hexafluoride SF 6
Sulfur is named first, since it lies below and to the left of fluorine in the periodic table. (The element that is first
in the name is also first in the formula.) The prefixes tell how many atoms of the second element there are in each
molecule.
EXAMPLE 6.4. Name P 2 O 3 .
Ans. Phosphorus lies to the left and below oxygen in the periodic table, so it is named first. The number of atoms of the
first element is specified because it is greater than one: diphosphorus trioxide.
EXAMPLE 6.5. Name a compound containing in each molecule (a) two oxygen atoms and a bromine atom and (b) one
nitrogen atom and three chlorine atoms.
Ans. (a) Bromine dioxide and (b) nitrogen trichloride. In BrO 2 , O is above Br but to its left in the periodic table. In NCl 3 ,
N is above Cl and to its left. When this situation arises with oxygen or fluorine, that element is written last; any other
such pair has the element to the left written first. That is the reason for the order of naming in BrO 2 and NCl 3 .
EXAMPLE 6.6. Name NH 3 .
Ans. Ammonia. The common name is used.
6.3. NAMING IONIC COMPOUNDS
Ionic compounds are composed of cations (positive ions) and anions (negative ions). The cation is always
named first, and then the anion is named. The name of the cation does not depend on the nature of the anion, and
the name of the anion does not depend on the nature of the cation.