Page 72 - Semiconductor For Micro- and Nanotechnology An Introduction For Engineers
P. 72
The Vibrating Uniform Lattice
unit cell = a
unit cell = a
slope = 0
ω k() ω k()
slope = v Optical
branch
slope = v
Acoustic
branch
Acoustic
branch
π π π π
– --- --- – --- ---
a a k a a k
X ∆ Γ ∆ X X ∆ Γ ∆ X
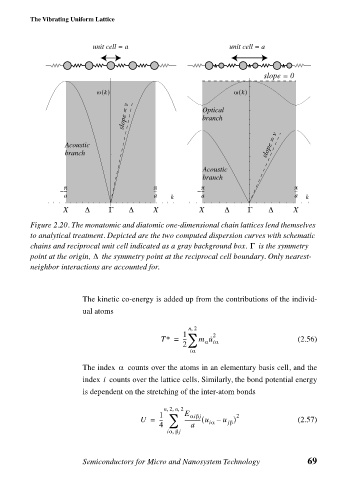
Figure 2.20. The monatomic and diatomic one-dimensional chain lattices lend themselves
to analytical treatment. Depicted are the two computed dispersion curves with schematic
Γ
chains and reciprocal unit cell indicated as a gray background box. is the symmetry
∆
point at the origin, the symmetry point at the reciprocal cell boundary. Only nearest-
neighbor interactions are accounted for.
The kinetic co-energy is added up from the contributions of the individ-
ual atoms
,
n 2
1 2
T ∗ = --- ∑ m u˙ (2.56)
α iα
2
iα
α
The index counts over the atoms in an elementary basis cell, and the
i
index counts over the lattice cells. Similarly, the bond potential energy
is dependent on the stretching of the inter-atom bonds
,,,
n 2 n 2
1 E αiβj 2
U = --- ∑ ------------ u –( iα u ) (2.57)
jβ
4 a
,
iαβj
Semiconductors for Micro and Nanosystem Technology 69