Page 144 - Sensing, Intelligence, Motion : How Robots and Humans Move in an Unstructured World
P. 144
VISION AND MOTION PLANNING 119
T
C
T
T i
Q
Q
L j
L j
C
X j
S
T i
X j
S
(a) (b)
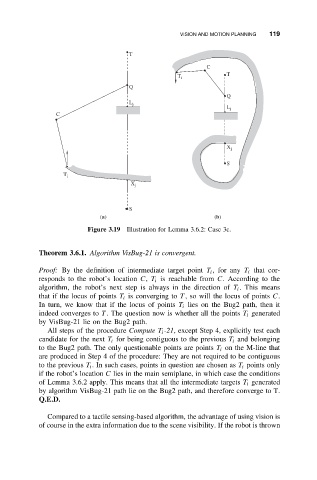
Figure 3.19 Illustration for Lemma 3.6.2: Case 3c.
Theorem 3.6.1. Algorithm VisBug-21 is convergent.
Proof: By the definition of intermediate target point T i ,for any T i that cor-
responds to the robot’s location C, T i is reachable from C. According to the
algorithm, the robot’s next step is always in the direction of T i . This means
that if the locus of points T i is converging to T , so will the locus of points C.
In turn, we know that if the locus of points T i lies on the Bug2 path, then it
indeed converges to T . The question now is whether all the points T i generated
by VisBug-21 lie on the Bug2 path.
All steps of the procedure Compute T i -21, except Step 4, explicitly test each
candidate for the next T i for being contiguous to the previous T i and belonging
to the Bug2 path. The only questionable points are points T i on the M-line that
are produced in Step 4 of the procedure: They are not required to be contiguous
to the previous T i . In such cases, points in question are chosen as T i points only
if the robot’s location C lies in the main semiplane, in which case the conditions
of Lemma 3.6.2 apply. This means that all the intermediate targets T i generated
by algorithm VisBug-21 path lie on the Bug2 path, and therefore converge to T.
Q.E.D.
Compared to a tactile sensing-based algorithm, the advantage of using vision is
of course in the extra information due to the scene visibility. If the robot is thrown