Page 141 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 141
102
Cha p te r
T w o
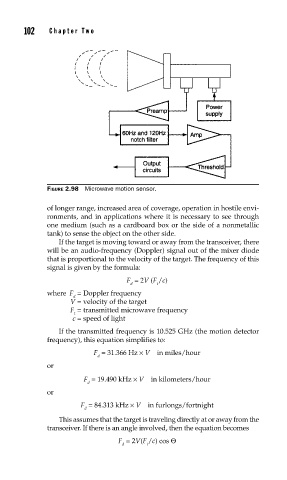
FIGURE 2.98 Microwave motion sensor.
of longer range, increased area of coverage, operation in hostile envi-
ronments, and in applications where it is necessary to see through
one medium (such as a cardboard box or the side of a nonmetallic
tank) to sense the object on the other side.
If the target is moving toward or away from the transceiver, there
will be an audio-frequency (Doppler) signal out of the mixer diode
that is proportional to the velocity of the target. The frequency of this
signal is given by the formula:
F = 2V (F /c)
d t
where F = Doppler frequency
d
V = velocity of the target
F = transmitted microwave frequency
t
c = speed of light
If the transmitted frequency is 10.525 GHz (the motion detector
frequency), this equation simplifies to:
F = 31.366 Hz × V in miles/hour
d
or
F = 19.490 kHz × V in kilometers/hour
d
or
F = 84.313 kHz × V in furlongs/fortnight
d
This assumes that the target is traveling directly at or away from the
transceiver. If there is an angle involved, then the equation becomes
F = 2V(F /c) cos Θ
d t