Page 260 - Sensors and Control Systems in Manufacturing
P. 260
220
F o u r
Cha p te r
Independently
selected by
system integrator Application
software
Functional
interface
Function calls
Independently or macros
selected by
vendor
Equipment
FIGURE 4.16 Bridges system for MAP protocol.
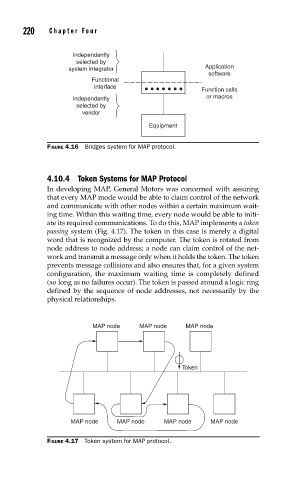
4.10.4 Token Systems for MAP Protocol
In developing MAP, General Motors was concerned with assuring
that every MAP mode would be able to claim control of the network
and communicate with other nodes within a certain maximum wait-
ing time. Within this waiting time, every node would be able to initi-
ate its required communications. To do this, MAP implements a token
passing system (Fig. 4.17). The token in this case is merely a digital
word that is recognized by the computer. The token is rotated from
node address to node address; a node can claim control of the net-
work and transmit a message only when it holds the token. The token
prevents message collisions and also ensures that, for a given system
configuration, the maximum waiting time is completely defined
(so long as no failures occur). The token is passed around a logic ring
defined by the sequence of node addresses, not necessarily by the
physical relationships.
MAP node MAP node MAP node
Token
MAP node MAP node MAP node MAP node
FIGURE 4.17 Token system for MAP protocol.