Page 189 -
P. 189
172 Chapter 6 Architectural design
Lexical Syntax Semantic
Analyzer Analyzer Analyzer
Pretty- Abstract Grammar
Printer Syntax Tree Definition Optimizer
Symbol Output Code
Editor Table Definition Generator
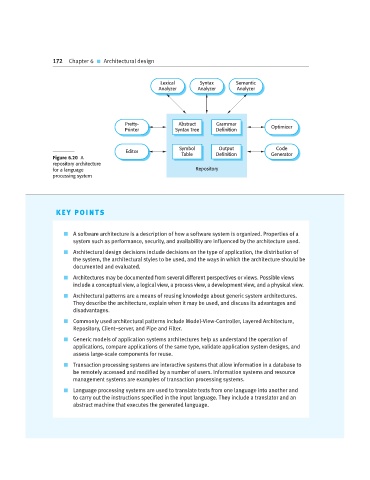
Figure 6.20 A
repository architecture
for a language Repository
processing system
KEY POINTS
A software architecture is a description of how a software system is organized. Properties of a
system such as performance, security, and availability are influenced by the architecture used.
Architectural design decisions include decisions on the type of application, the distribution of
the system, the architectural styles to be used, and the ways in which the architecture should be
documented and evaluated.
Architectures may be documented from several different perspectives or views. Possible views
include a conceptual view, a logical view, a process view, a development view, and a physical view.
Architectural patterns are a means of reusing knowledge about generic system architectures.
They describe the architecture, explain when it may be used, and discuss its advantages and
disadvantages.
Commonly used architectural patterns include Model-View-Controller, Layered Architecture,
Repository, Client–server, and Pipe and Filter.
Generic models of application systems architectures help us understand the operation of
applications, compare applications of the same type, validate application system designs, and
assess large-scale components for reuse.
Transaction processing systems are interactive systems that allow information in a database to
be remotely accessed and modified by a number of users. Information systems and resource
management systems are examples of transaction processing systems.
Language processing systems are used to translate texts from one language into another and
to carry out the instructions specified in the input language. They include a translator and an
abstract machine that executes the generated language.