Page 332 -
P. 332
12.2 Safety specification 315
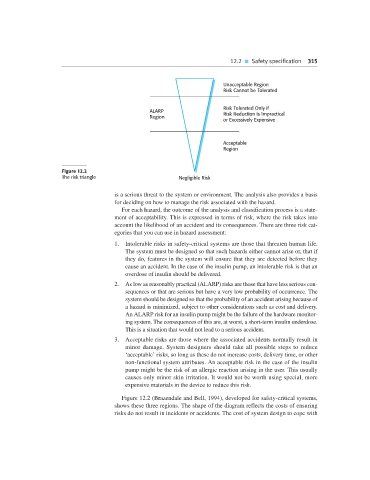
Unacceptable Region
Risk Cannot be Tolerated
Risk Tolerated Only if
ALARP Risk Reduction is Impractical
Region
or Excessively Expensive
Acceptable
Region
Figure 12.2
The risk triangle Negligible Risk
is a serious threat to the system or environment. The analysis also provides a basis
for deciding on how to manage the risk associated with the hazard.
For each hazard, the outcome of the analysis and classification process is a state-
ment of acceptability. This is expressed in terms of risk, where the risk takes into
account the likelihood of an accident and its consequences. There are three risk cat-
egories that you can use in hazard assessment:
1. Intolerable risks in safety-critical systems are those that threaten human life.
The system must be designed so that such hazards either cannot arise or, that if
they do, features in the system will ensure that they are detected before they
cause an accident. In the case of the insulin pump, an intolerable risk is that an
overdose of insulin should be delivered.
2. As low as reasonably practical (ALARP) risks are those that have less serious con-
sequences or that are serious but have a very low probability of occurrence. The
system should be designed so that the probability of an accident arising because of
a hazard is minimized, subject to other considerations such as cost and delivery.
An ALARP risk for an insulin pump might be the failure of the hardware monitor-
ing system. The consequences of this are, at worst, a short-term insulin underdose.
This is a situation that would not lead to a serious accident.
3. Acceptable risks are those where the associated accidents normally result in
minor damage. System designers should take all possible steps to reduce
‘acceptable’ risks, so long as these do not increase costs, delivery time, or other
non-functional system attributes. An acceptable risk in the case of the insulin
pump might be the risk of an allergic reaction arising in the user. This usually
causes only minor skin irritation. It would not be worth using special, more
expensive materials in the device to reduce this risk.
Figure 12.2 (Brazendale and Bell, 1994), developed for safety-critical systems,
shows these three regions. The shape of the diagram reflects the costs of ensuring
risks do not result in incidents or accidents. The cost of system design to cope with