Page 53 -
P. 53
24 PART ONE THE PRODUCT AND THE PROCESS
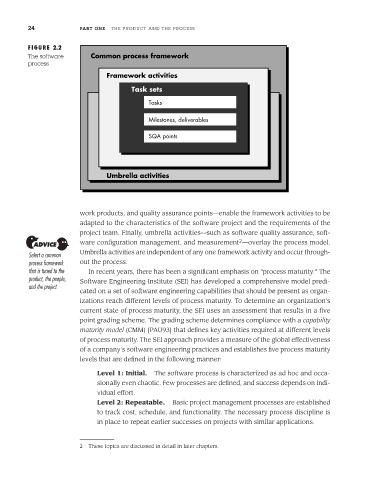
FIGURE 2.2
The software Common process framework
process
Framework activities
Task sets
Tasks
Milestones, deliverables
SQA points
Umbrella activities
work products, and quality assurance points—enable the framework activities to be
adapted to the characteristics of the software project and the requirements of the
project team. Finally, umbrella activities—such as software quality assurance, soft-
2
ware configuration management, and measurement —overlay the process model.
Umbrella activities are independent of any one framework activity and occur through-
Select a common
process framework out the process.
that is tuned to the In recent years, there has been a significant emphasis on “process maturity.” The
product, the people, Software Engineering Institute (SEI) has developed a comprehensive model predi-
and the project.
cated on a set of software engineering capabilities that should be present as organ-
izations reach different levels of process maturity. To determine an organization’s
current state of process maturity, the SEI uses an assessment that results in a five
point grading scheme. The grading scheme determines compliance with a capability
maturity model (CMM) [PAU93] that defines key activities required at different levels
of process maturity. The SEI approach provides a measure of the global effectiveness
of a company's software engineering practices and establishes five process maturity
levels that are defined in the following manner:
Level 1: Initial. The software process is characterized as ad hoc and occa-
sionally even chaotic. Few processes are defined, and success depends on indi-
vidual effort.
Level 2: Repeatable. Basic project management processes are established
to track cost, schedule, and functionality. The necessary process discipline is
in place to repeat earlier successes on projects with similar applications.
2 These topics are discussed in detail in later chapters.