Page 71 -
P. 71
42 PART ONE THE PRODUCT AND THE PROCESS
confining software engineering activities to a sequence of events, it defines a net-
work of activities. Each activity on the network exists simultaneously with other activ-
ities. Events generated within a given activity or at some other place in the activity
network trigger transitions among the states of an activity.
2.8 COMPONENT-BASED DEVELOPMENT
Object-oriented technologies (Part Four of this book) provide the technical frame-
work for a component-based process model for software engineering. The object-
oriented paradigm emphasizes the creation of classes that encapsulate both data and
the algorithms used to manipulate the data. If properly designed and implemented,
object-oriented classes are reusable across different applications and computer-based
system architectures.
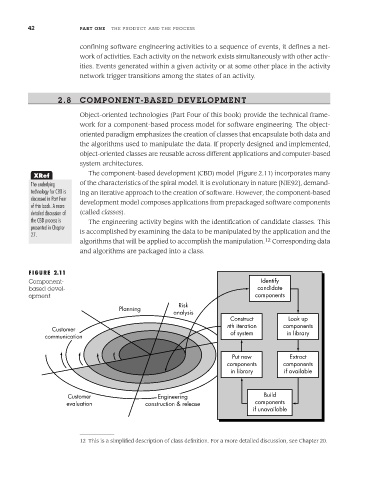
The component-based development (CBD) model (Figure 2.11) incorporates many
XRef
The underlying of the characteristics of the spiral model. It is evolutionary in nature [NIE92], demand-
technology for CBD is ing an iterative approach to the creation of software. However, the component-based
discussed in Part Four development model composes applications from prepackaged software components
of this book. A more
detailed discussion of (called classes).
the CBD process is The engineering activity begins with the identification of candidate classes. This
presented in Chapter is accomplished by examining the data to be manipulated by the application and the
27.
algorithms that will be applied to accomplish the manipulation. 12 Corresponding data
and algorithms are packaged into a class.
FIGURE 2.11
Component- Identify
based devel- candidate
opment components
Risk
Planning
analysis
Construct Look up
nth iteration components
Customer
communication of system in library
Put new Extract
components components
in library if available
Customer Engineering Build
evaluation construction & release components
if unavailable
12 This is a simplified description of class definition. For a more detailed discussion, see Chapter 20.