Page 112 - Software and Systems Requirements Engineering in Practice
P. 112
q
e
R
u
e
r
i
e
t
p
r
:
4
e
d
o
l
g
n
i
n
e
m
t
M
s
h
C
C h a p t e r 4 : R e q u i r e m e n t s M o d e l i n g 81 81
a
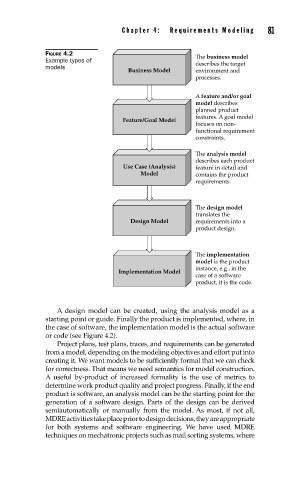
FIGURE 4.2 The business model
Example types of describes the target
models
Business Model environment and
processes.
A feature and/or goal
model describes
planned product
features. A goal model
Feature/Goal Model
focuses on non-
functional requirement
constraints.
The analysis model
describes each product
Use Case (Analysis) feature in detail and
Model contains the product
requirements.
The design model
translates the
Design Model requirements into a
product design.
The implementation
model is the product
instance, e.g., in the
Implementation Model
case of a software
product, it is the code.
A design model can be created, using the analysis model as a
starting point or guide. Finally the product is implemented, where, in
the case of software, the implementation model is the actual software
or code (see Figure 4.2).
Project plans, test plans, traces, and requirements can be generated
from a model, depending on the modeling objectives and effort put into
creating it. We want models to be sufficiently formal that we can check
for correctness. That means we need semantics for model construction.
A useful by-product of increased formality is the use of metrics to
determine work product quality and project progress. Finally, if the end
product is software, an analysis model can be the starting point for the
generation of a software design. Parts of the design can be derived
semiautomatically or manually from the model. As most, if not all,
MDRE activities take place prior to design decisions, they are appropriate
for both systems and software engineering. We have used MDRE
techniques on mechatronic projects such as mail sorting systems, where