Page 201 - Software and Systems Requirements Engineering in Practice
P. 201
i
t
a
l
y
t
t
A
t
e
a
p
r
:
u
5
r
r
e
u
i
m
t
s
e
n
u
t
i
b
e
e
q
R
C h a p t e r 5 : Q Q u a l i t y A t t r i b u t e R e q u i r e m e n t s 167 167
C
h
Database Network
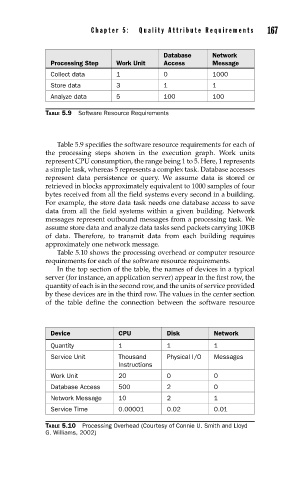
Processing Step Work Unit Access Message
Collect data 1 0 1000
Store data 3 1 1
Analyze data 5 100 100
TABLE 5.9 Software Resource Requirements
Table 5.9 specifies the software resource requirements for each of
the processing steps shown in the execution graph. Work units
represent CPU consumption, the range being 1 to 5. Here, 1 represents
a simple task, whereas 5 represents a complex task. Database accesses
represent data persistence or query. We assume data is stored or
retrieved in blocks approximately equivalent to 1000 samples of four
bytes received from all the field systems every second in a building.
For example, the store data task needs one database access to save
data from all the field systems within a given building. Network
messages represent outbound messages from a processing task. We
assume store data and analyze data tasks send packets carrying 10KB
of data. Therefore, to transmit data from each building requires
approximately one network message.
Table 5.10 shows the processing overhead or computer resource
requirements for each of the software resource requirements.
In the top section of the table, the names of devices in a typical
server (for instance, an application server) appear in the first row, the
quantity of each is in the second row, and the units of service provided
by these devices are in the third row. The values in the center section
of the table define the connection between the software resource
Device CPU Disk Network
Quantity 1 1 1
Service Unit Thousand Physical I/O Messages
Instructions
Work Unit 20 0 0
Database Access 500 2 0
Network Message 10 2 1
Service Time 0.00001 0.02 0.01
TABLE 5.10 Processing Overhead (Courtesy of Connie U. Smith and Lloyd
G. Williams, 2002)