Page 183 - Soil Degradation, Conservation and Remediation
P. 183
172 6 Soil Pollution
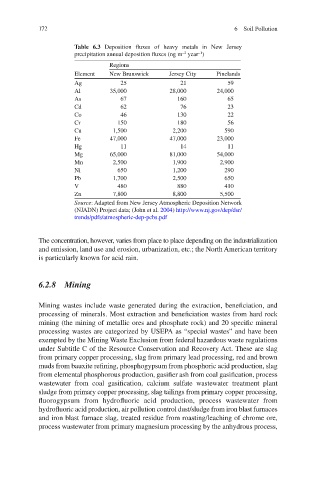
Table 6.3 Deposition fluxes of heavy metals in New Jersey
−2
−1
precipitation annual deposition fluxes (ng m year )
Regions
Element New Brunswick Jersey City Pinelands
Ag 25 21 59
Al 35,000 28,000 24,000
As 67 160 65
Cd 62 76 23
Co 46 130 22
Cr 150 180 56
Cu 1,500 2,200 590
Fe 47,000 47,000 23,000
Hg 11 14 11
Mg 65,000 81,000 54,000
Mn 2,500 1,900 2,900
Ni 650 1,200 290
Pb 1,700 2,500 650
V 480 880 410
Zn 7,800 8,800 5,500
Source : Adapted from New Jersey Atmospheric Deposition Network
(NJADN ) Project data; (John et al. 2004 ) http://www.nj.gov/dep/dsr/
trends/pdfs/atmospheric-dep-pcbs.pdf
The concentration, however, varies from place to place depending on the industrialization
and emission, land use and erosion, urbanization, etc.; the North American territory
is particularly known for acid rain.
6.2.8 Mining
Mining wastes include waste generated during the extraction, benefi ciation, and
processing of minerals. Most extraction and beneficiation wastes from hard rock
mining (the mining of metallic ores and phosphate rock) and 20 specifi c mineral
processing wastes are categorized by USEPA as “special wastes” and have been
exempted by the Mining Waste Exclusion from federal hazardous waste regulations
under Subtitle C of the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act. These are slag
from primary copper processing, slag from primary lead processing, red and brown
muds from bauxite refining, phosphogypsum from phosphoric acid production, slag
from elemental phosphorous production, gasifier ash from coal gasifi cation, process
wastewater from coal gasification, calcium sulfate wastewater treatment plant
sludge from primary copper processing, slag tailings from primary copper processing,
fluorogypsum from hydrofluoric acid production, process wastewater from
hydrofluoric acid production, air pollution control dust/sludge from iron blast furnaces
and iron blast furnace slag, treated residue from roasting/leaching of chrome ore,
process wastewater from primary magnesium processing by the anhydrous process,