Page 25 - Soil Degradation, Conservation and Remediation
P. 25
10 1 Soil Resources and Soil Degradation
40
35
30
Area, million Km 2 20
25
15
10
5
0
I II III IV V VI VII VIII IX
Land quality classes
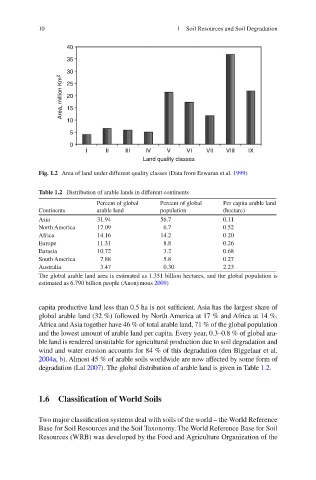
Fig. 1.2 Area of land under different quality classes (Data from Eswaran et al. 1999 )
Table 1.2 Distribution of arable lands in different continents
Percent of global Percent of global Per capita arable land
Continents arable land population (hectare)
Asia 31.94 56.7 0.11
North America 17.09 6.7 0.52
Africa 14.16 14.2 0.20
Europe 11.31 8.8 0.26
Eurasia 10.72 3.2 0.68
South America 7.88 5.8 0.27
Australia 3.47 0.30 2.23
The global arable land area is estimated as 1.351 billion hectares, and the global population is
estimated as 6.790 billion people (Anonymous 2009 )
capita productive land less than 0.5 ha is not sufficient. Asia has the largest share of
global arable land (32 %) followed by North America at 17 % and Africa at 14 %.
Africa and Asia together have 46 % of total arable land, 71 % of the global population
and the lowest amount of arable land per capita. Every year, 0.3–0.8 % of global ara-
ble land is rendered unsuitable for agricultural production due to soil degradation and
wind and water erosion accounts for 84 % of this degradation (den Biggelaar et al.
2004a , b ). Almost 45 % of arable soils worldwide are now affected by some form of
degradation (Lal 2007 ). The global distribution of arable land is given in Table 1.2 .
1.6 Classification of World Soils
Two major classification systems deal with soils of the world – the World Reference
Base for Soil Resources and the Soil Taxonomy. The World Reference Base for Soil
Resources (WRB) was developed by the Food and Agriculture Organization of the