Page 125 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 125
112 Soil and Water Contamination
1.40
6642 6642 6642
Water oxidised
1.20
1.00
0.80
0.60
0.40
2-
SO 4
Eh (Volt) 0.20 S 0
0.00
H SO 42 (aq)
-0.20
-0.40
-
HS
-0.60
2-
S
-0.80
Water reduced
-1.00
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
pH
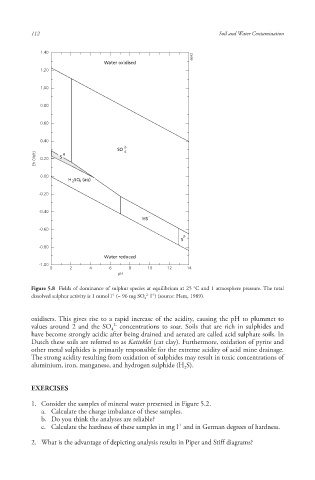
Figure 5.8 Fields of dominance of sulphur species at equilibrium at 25 °C and 1 atmosphere pressure. The total
-1
2- -1
dissolved sulphur activity is 1 mmol l (= 96 mg SO 4 l ) (source: Hem, 1989).
oxidisers. This gives rise to a rapid increase of the acidity , causing the pH to plummet to
2-
values around 2 and the SO concentrations to soar. Soils that are rich in sulphides and
4
have become strongly acidic after being drained and aerated are called acid sulphate soils . In
Dutch these soils are referred to as Katteklei (cat clay). Furthermore, oxidation of pyrite and
other metal sulphides is primarily responsible for the extreme acidity of acid mine drainage.
The strong acidity resulting from oxidation of sulphides may result in toxic concentrations of
aluminium , iron , manganese , and hydrogen sulphide (H S).
2
EXERCISES
1. Consider the samples of mineral water presented in Figure 5.2.
a. Calculate the charge imbalance of these samples.
b. Do you think the analyses are reliable?
-1
c. Calculate the hardness of these samples in mg l and in German degrees of hardness.
2. What is the advantage of depicting analysis results in Piper and Stiff diagrams ?
10/1/2013 6:44:30 PM
Soil and Water.indd 124
Soil and Water.indd 124 10/1/2013 6:44:30 PM