Page 78 - Soil and water contamination, 2nd edition
P. 78
Environmental compartments 65
Accidental spills can cause severe pollution of surface water. They may occur due to, for
example, leaks of process chemicals and products from industrial installations, release of
contaminated firefighting water during fire abatement, or failures of tailing dams of mine
reservoirs. Notorious examples are the Sandoz accident in Basle (river Rhine ), Switzerland
in 1986, the cyanide spill at Baia Mare (Tisza river), Romania in 2000, and the benzene
and nitrobenzene spill in Jilin (Songhua river ), China in 2005 (see Section 10.2 for further
details). Spills may also occur at a more local scale : for example, car accidents.
Pollutants discharged into surface water may partly be retained in the bed sediments . In
this case, the bed sediments act as a sink for pollutants. A considerable stock of pollutants
may accumulate over the years and as soon as the pollutant concentrations in the surface
water fall, these pollutants may be re-released from the bed sediments. In such cases, bed
sediments may act like a diffuse source of pollutants. This type of source is also refereed
to as internal loading . Internal loading also encompasses the release of nutrients and other
pollutants due to the decomposition of internally produced organic matter (e.g. litter from
aquatic plants and algae ).
3.4.4 Physico-chemical conditions in surface water
An important parameter in surface water quality studies is water temperature , since it
affects many physical, chemical, and biological processes. It influences, amongst others,
the dissolved oxygen concentration, the growth rate and rate of photosynthesis of algae
and other aquatic plants, and the decomposition rate of organic matter. The temperature
of surface water generally follows seasonal and local weather patterns, although the course
of water temperature is subdued and lags behind the air temperature. Surface water bodies
exposed to direct sunlight may be up to 10 °C warmer than shaded water bodies. In deep
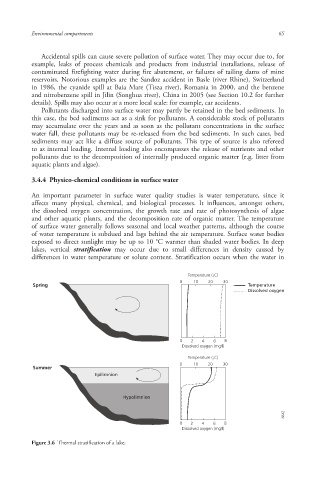
lakes , vertical stratification may occur due to small differences in density caused by
differences in water temperature or solute content. Stratification occurs when the water in
Temperature (¡C)
0 10 20 30
Spring Temperature
Dissolved oxygen
0 2 4 6 8
Dissolved oxygen (mg/l)
Temperature (¡C)
0 10 20 30
Summer
Epilimnion
Hypolimnion
6642 6642 6642
0 2 4 6 8
Dissolved oxygen (mg/l)
Figure 3.6 Thermal stratification of a lake.
10/1/2013 6:44:22 PM
Soil and Water.indd 77 10/1/2013 6:44:22 PM
Soil and Water.indd 77