Page 18 - Standard Handbook Of Petroleum & Natural Gas Engineering
P. 18
Geometry 7
changed when moved around the plane, if its magnitude and angular orientation
with respect to the x-axis is kept constant. The initial point of v may therefore
be placed at the origin of the coordinate system and?’may be denoted by
d= < a,b >
where a is the x-component and b is the y-component of the terminal point.
The magnitude may then be determined by the Pythagorean theorem
For every pair of vectors (xI,yI) and (x2,y2), the vector sum is given by (x, + xp,
y1 + y2). The scalar product of a vector P = (x,y) and a real number (a scalar) r
is rP = (rx,ry). Also see the discussion of polar coordinates in the section
“Trigonometry” and Chapter 2, “Basic Mechanics.”
Lengths and Areas of Plane Figures [l]
(For definitions of trigonometric functions, see “Trigonometry.”)
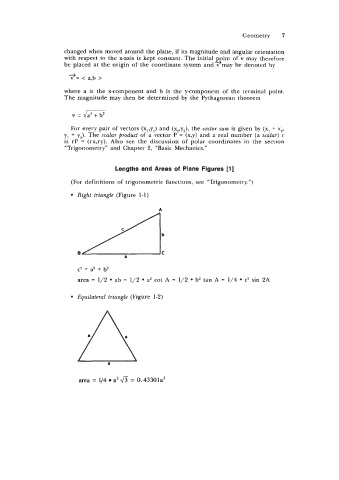
Right triangle (Figure 1-1)
A
c2 = a2 + b2
area = 1/2 ab = 1/2 a2 cot A = 1/2 b2 tan A = 1/4 c2 sin 2A
Equilateral triangle (Figure 1-2)
area = 114 a2 & = 0. 43301a2