Page 430 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 430
394 Production
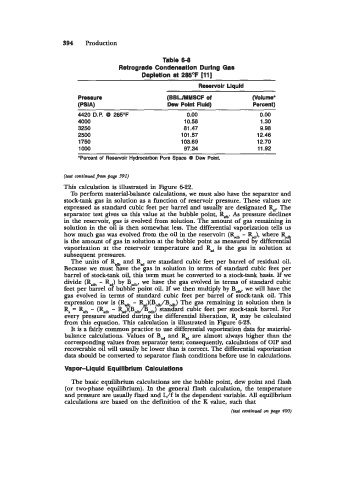
Table 6-8
Retrograde Condensation During Gas
Depletion at 285OF [ll]
Reservoir Liquid
Pressure (BBLJMMSCF d (Volume'
(PSIA) Dew Point Fluid) Percent)
4420 D.P. 0 285°F 0.00 0.00
4000 10.58 1.30
3250 81.47 9.98
2500 101.57 12.46
1750 103.69 12.70
1 000 97.34 11.92
*Percent of Reservoir Hydrocarbon Pore Space QD Dew Point.
(text continued jhm page 391)
This calculation is illustrated in Figure 622.
To perform material-balance calculations, we must also have the separator and
stock-tank gas in solution as a function of reservoir pressure. These values are
expressed as standard cubic feet per barrel and usually are designated R,r The
separator test gives us this value at the bubble point, Rdb' As pressure declines
in the reservoir, gas is evolved from solution. The amount of gas remaining in
solution in the oil is then somewhat less. The differential vaporization tells us
how much gas was evolved from the oil in the reservoir: (Rd - R,), where Rdb
is the amount of gas in solution at the bubble point as measured by differential
vaporization at the reservoir temperature and R, is the gas in solution at
subsequent pressures.
The units of R and Rd are standard cubic feet per barrel of residual oil.
Because we must gave the gas in solution in terms of standard cubic feet per
barrel of stock-tank oil, this term must be converted to a stock-tank basis. If we
divide (R,db - R,) by B,,, we have the gas evolved in terms of standard cubic
feet per barrel of bubble point oil. If we then multiply by B,, we will have the
gas evolved in terms of standard cubic feet per barrel of stock-tank oil. This
expression now is (R - Rd)(Bom/Bodb) The gas remaining in solution then is
R, = R, - (Rdb - R,TBd/Bd) standard cubic feet per stock-tank barrel. For
every pressure studied during the differential liberation, R, may be calculated
from this equation. This calculation is illustrated in Figure 6-23.
It is a fairly common practice to use differential vaporization data for material-
balance calculations. Values of B, and R, are almost always higher than the
corresponding values from separator tests; consequently, calculations of OIP and
recoverable oil will usually be lower than is correct. The differential vaporization
data should be converted to separator flash conditions before use in calculations.
Vapor-Liquid Equilibrium Calculations
The basic equilibrium calculations are the bubble point, dew point and flash
(or two-phase equilibrium). In the general flash calculation, the temperature
and pressure are usually fixed and L/f is the dependent variable. All equilibrium
calculations are based on the definition of the K value, such that
(tat continusd on pogs 400)