Page 439 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 439
Properties of Hydrocarbon Mixtures 401
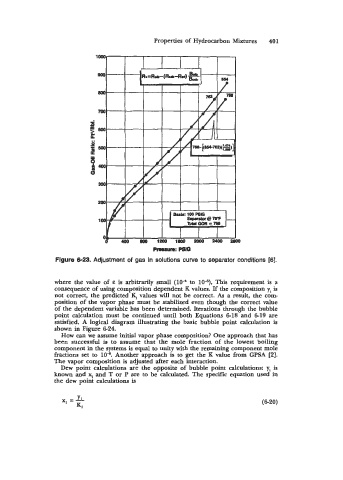
Figure 6-23. Adjustment of gas in solutions curve to separator conditions [6].
where the value of E is arbitrarily small (lo4 to lo4), This requirement is a
consequence of using composition dependent K values. If the composition yi is
not correct, the predicted I$ values will not be correct. As a result, the com-
position of the vapor phase must be stabilized even though the correct value
of the dependent variable has been determined. Iterations through the bubble
point calculation must be continued until both Equations 6-18 and 6-19 are
satisfied. A logical diagram illustrating the basic bubble point calculation is
shown in Figure 6-24.
How can we assume initial vapor phase composition? One approach that has
been successful is to assume that the mole fraction of the lowest boiling
component in the systems is equal to unity with the remaining component mole
fractions set to Another approach is to get the K value from GPSA [2].
The vapor composition is adjusted after each interaction.
Dew point calculations are the opposite of bubble point calculations: yi is
known and xi and T or P are to be calculated. The specific equation used in
the dew point calculations is