Page 441 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 441
Properties of Hydrocarbon Mixtures 403
( ) initial assumption of
dependent variable
or T, (PI
Assume IlquM
phase composition
and Ex, I
I Calculate XI
,
xI
Adjust dependent
Adjust dependent Exit wlth xI ,
Exit
wlth
T
varlable P. and T
P.
and
varlable
f
Adjust llquld
phase composltbn
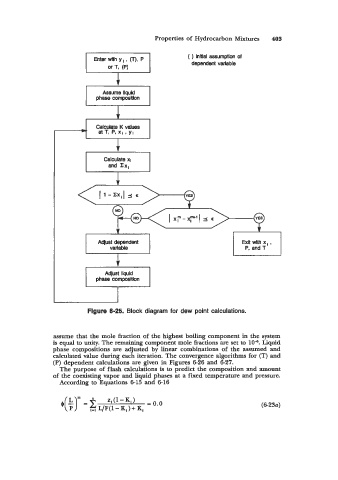
Figure 6-25. Block diagram for dew point calculations.
assume that the mole fraction of the highest boiling component in the system
is equal to unity. The remaining component mole fractions are set to lo4. Liquid
phase compositions are adjusted by linear combinations of the assumed and
calculated value during each iteration. The convergence algorithms for (T) and
(P) dependent calculations are given in Figures 6-26 and 6-27.
The purpose of flash calculations is to predict the composition and amount
of the coexisting vapor and liquid phases at a fixed temperature and pressure.
According to Equations 6-15 and 6-16
(6-23a)