Page 539 - Standard Handbook Petroleum Natural Gas Engineering VOLUME2
P. 539
Flow of Fluids 493
2
10 4 10"
4
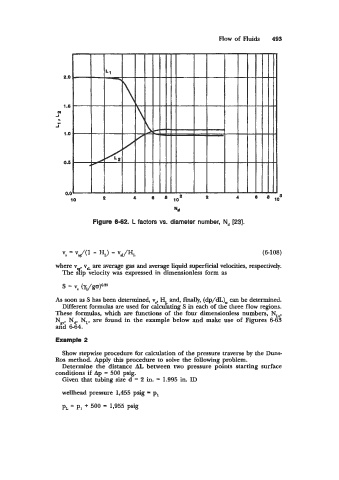
Figure 6-62. L factors vs. diameter number, N, [23].
V, = vJ(1 - HL) - vIJH, (6-108)
where v , vsL are average gas and average liquid superficial velocities, respectively.
The 3ip velocity was expressed in dimensionless form as
s = vs (yJga)0.*5
As soon as S has been determined, v,, H, and, fmlly, (dp/dL), can be determined.
Different formulas are used for calculating S in each of the three flow regions.
These formulas, which are functions of the four dimensionless numbers, NLv,
N,, N,, N,, are found in the example below and make use of Figures 6-63
and 6-64.
Example 2
Show stepwise procedure for calculation of the pressure traverse by the Duns-
Ros method. Apply this procedure to solve the following problem.
Determine the distance AL between two pressure points starting surface
conditions if Ap = 500 psig.
Given that tubing size d = 2 in. = 1.995 in. ID
wellhead pressure 1,455 psig = p1
p, = p1 + 500 = 1,955 psig