Page 21 - Structural Steel Designers Handbook AISC, AASHTO, AISI, ASTM, and ASCE-07 Design Standards
P. 21
Brockenbrough_Ch01.qxd 9/29/05 4:59 PM Page 1.19
PROPERTIES OF STRUCTURAL STEELS AND EFFECTS OF STEELMAKING AND FABRICATION
STRUCTURAL STEELS, STEELMAKING, AND FABRICATION 1.19
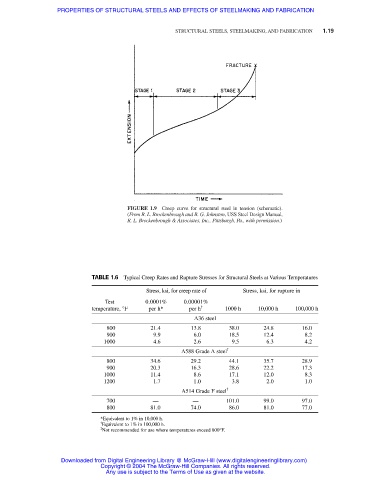
FIGURE 1.9 Creep curve for structural steel in tension (schematic).
(From R. L. Brockenbrough and B. G. Johnston, USS Steel Design Manual,
R. L. Brockenbrough & Associates, Inc., Pittsburgh, Pa., with permission.)
TABLE 1.6 Typical Creep Rates and Rupture Stresses for Structural Steels at Various Temperatures
Stress, ksi, for creep rate of Stress, ksi, for rupture in
Test 0.0001% 0.00001%
temperature, °F per h* per h † 1000 h 10,000 h 100,000 h
A36 steel
800 21.4 13.8 38.0 24.8 16.0
900 9.9 6.0 18.5 12.4 8.2
1000 4.6 2.6 9.5 6.3 4.2
A588 Grade A steel †
800 34.6 29.2 44.1 35.7 28.9
900 20.3 16.3 28.6 22.2 17.3
1000 11.4 8.6 17.1 12.0 8.3
1200 1.7 1.0 3.8 2.0 1.0
A514 Grade F steel †
700 — — 101.0 99.0 97.0
800 81.0 74.0 86.0 81.0 77.0
*Equivalent to 1% in 10,000 h.
†
Equivalent to 1% in 100,000 h.
‡
Not recommended for use where temperatures exceed 800°F.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.