Page 261 - Structural Steel Designers Handbook AISC, AASHTO, AISI, ASTM, and ASCE-07 Design Standards
P. 261
Brockenbrough_Ch05.qxd 9/29/05 5:12 PM Page 5.41
CRITERIA FOR BUILDING DESIGN
CRITERIA FOR BUILDING DESIGN 5.41
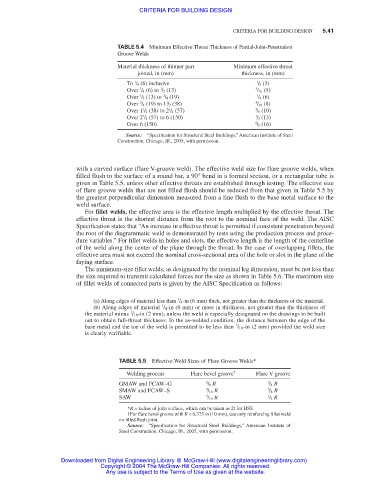
TABLE 5.4 Minimum Effective Throat Thickness of Partial-Joint-Penetration
Groove Welds
Material thickness of thinner part Minimum effective throat
joined, in (mm) thickness, in (mm)
1
To / 4 (6) inclusive 1 / 8 (3)
Over / 4 (6) to / 2 (13) 3 / 16 (5)
1
1
3
1
Over / 2 (13) to / 4 (19) 1 / 4 (6)
Over / 4 (19) to 1 / 2 (38) 5 / 16 (8)
3
1
1
1
Over 1 / 2 (38) to 2 / 4 (57) 3 / 8 (10)
1
Over 2 / 4 (57) to 6 (150) 1 / 2 (13)
Over 6 (150) 5 / 8 (16)
Source: “Specification for Structural Steel Buildings,” American Institute of Steel
Construction, Chicago, Ill., 2005, with permission.
with a curved surface (flare V-groove weld). The effective weld size for flare groove welds, when
filled flush to the surface of a round bar, a 90° bend in a formed section, or a rectangular tube is
given in Table 5.5, unless other effective throats are established through testing. The effective size
of flare groove welds that are not filled flush should be reduced from that given in Table 5.5 by
the greatest perpendicular dimension measured from a line flush to the base metal surface to the
weld surface.
For fillet welds, the effective area is the effective length multiplied by the effective throat. The
effective throat is the shortest distance from the root to the nominal face of the weld. The AISC
Specification states that “An increase in effective throat is permitted if consistent penetration beyond
the root of the diagrammatic weld is demonstrated by tests using the production process and proce-
dure variables.” For fillet welds in holes and slots, the effective length is the length of the centerline
of the weld along the center of the plane through the throat. In the case of overlapping fillets, the
effective area must not exceed the nominal cross-sectional area of the hole or slot in the plane of the
faying surface.
The minimum-size fillet welds, as designated by the nominal leg dimension, must be not less than
the size required to transmit calculated forces nor the size as shown in Table 5.6. The maximum size
of fillet welds of connected parts is given by the AISC Specification as follows:
1
(a) Along edges of material less than / 4-in (6 mm) thick, not greater than the thickness of the material.
1
(b) Along edges of material / 4-in (6 mm) or more in thickness, not greater than the thickness of
1
the material minus / 16-in (2 mm), unless the weld is especially designated on the drawings to be built
out to obtain full-throat thickness. In the as-welded condition, the distance between the edge of the
1
base metal and the toe of the weld is permitted to be less than / 16-in (2 mm) provided the weld size
is clearly verifiable.
TABLE 5.5 Effective Weld Sizes of Flare Groove Welds*
Welding process Flare bevel groove † Flare V groove
GMAW and FCAW–G 5 / 8 R 3 / 4 R
SMAW and FCAW–S 5 / 16 R 5 / 8 R
SAW 5 / 16 R 1 / 2 R
*R = radius of joint surface, which can be taken as 2t for HSS.
†For flare bevel groove with R < 0.375 in (10 mm), use only reinforcing fillet weld
on filled flush joint.
Source: “Specification for Structural Steel Buildings,” American Institute of
Steel Construction, Chicago, Ill., 2005, with permission.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.