Page 101 - Sumatra Geology, Resources and Tectonic Evolution
P. 101
88 CHAPTER 7
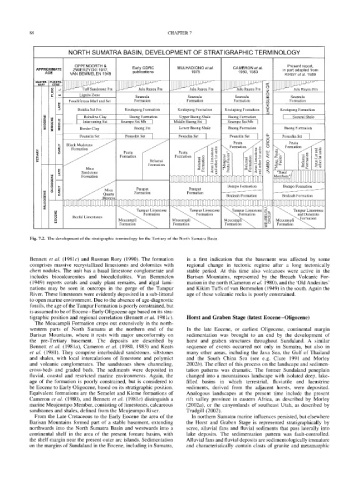
NORTH SUMATRA BASIN, DEVELOPMENT OF STRATIGRAPHIC TERMINOLOGY
OPPENOORTH & Present report,
APPROXIMATE ZWIERZYCKI 1917, Early GDRC MULHADIONO et al. CAMERON et al. in part adapted from
AGE VAN BEMMELEN 1949 publications 1978 1980, 1983 KIRBY et al. 1989
QUATER- PLEISTO- Ii : ' --
NARY CENE I
6 - ~ e F m Julu Rayeu Fm ~ J u l u Rayeu Fm Z
~. tu Lignite Zone Seureula Seureula Seureula O Seureula
'r
09
t,, Fossiliferous Marl and Sst Formation Formation Formation D Formation
v
'~ Rotalia Sst Fm Keutapang Formation Keutapang Formation Keutapang Formation O Keutapang Formation
Robulina Clay Baong Formation Upper Baong Shale Baong Formation [ Securai Shale
~ ~ ~,
o ~ ~ Intervening Sst Seumpo Sst Mb I Middle Baong Sst I Seumpo Sst Mb I
z~O~ Border Clay Baong Fm Lower Baong Shale Baong Formation Baong Formation
Peunulin Sst Peunulin Sst Peunulin Sst Peunulin Sst a. Peunu|in Sst
Peutu ~ O Peutu
Black Mudstone
~ ~ " = Formation/ ~ (.9 ~ Formation / .~ ~
Peutu Peutu ~'~ = ~== "E UJ 2= ~ J N~
Formation Formation - ~ ~ _ % ~ ~ ~ ~-~ ~ ~ o = ~ .- ~ ~ =
= ~
~
Belumai :~ ~ E'~ ~ 0 ~ ~ ; z =
Formation "~ = --
Mica m ~, < ~=
ILl
,,,,~ Sandstone
,,=,
~ Parapat Parapat Bampo Formation Bampo Formation
Formation Formation Bruksah Formation Bruksah Formation
-I
I1,1 Reefal Limestones ~ Formation ~ Formation "x...F.ormation ~ ~ ~ and Dolomite
e, Meucam.pli ~ Meucampli ~ Meucampll"-~. N Meucamph ~"'~--
D a: e
~
nl
Formation ~ Formation ~ Formation "~ Formation
Fig. 7.2. The development of the stratigraphic terminology for the Tertiary of the North Sumatra Basin.
Bennett et al. (1981c) and Rusman Rory (1990). The formation is a first indication that the basement was affected by some
comprises massive recrystallized limestones and dolomites with regional change in tectonic regime after a long tectonically
chert nodules. The unit has a basal limestone conglomerate and stable period. At this time also volcanoes were active in the
includes biocalcarenites and biocalcilutites. Van Bemmelen Barisan Mountains, represented by the Breueh Volcanic For-
(1949) reports corals and coaly plant remains, and algal lami- mation in the north (Cameron et al. 1980), and the 'Old Andesites'
nations may be seen in outcrops in the gorge of the Tampur and Kikim Tufts of van Bemmelen (1949) in the south. Again the
River. These limestones were evidently deposited in a sub-littoral age of these volcanic rocks is poorly constrained.
to open marine environment. Due to the absence of age-diagnostic
fossils, the age of the Tampur Formation is poorly constrained, but
is assumed to be of Eocene-Early Oligocene age based on its stra-
tigraphic position and regional correlation (Bennett et al. 1981c). Horst and Graben Stage (latest Eocene-Oligocene)
The Meucampli Formation crops out extensively in the north-
western parts of North Sumatra at the northern end of the In the late Eocene, or earliest Oligocene, continental margin
Barisan Mountains, where it rests with major unconformity on sedimentation was brought to an end by the development of
the pre-Tertiary basement. The deposits are described by horst and graben structures throughout Sundaland. A similar
Bennett et al. (1981a), Cameron et al. (1980, 1983) and Keats sequence of events occurred not only in Sumatra, but also in
et al. (1981). They comprise interbedded sandstones, siltstones many other areas, including the Java Sea, the Gulf of Thailand
and shales, with local intercalations of limestone and polymict and the South China Sea (see e.g. Clure 1991 and Morley
and volcanic conglomerates. The sandstones show channeling, 2002b). The effect of this process on the landscape and sedimen-
cross-beds and graded beds. The sediments were deposited in tation patterns was dramatic. The former Sundaland peneplain
fluvial, coastal and restricted marine environments. Again, the changed into a mountainous landscape with isolated deep, lake-
age of the formation is poorly constrained, but is considered to filled basins in which terrestrial, fluviatile and lacustrine
be Eocene to Early Oligocene, based on its stratigraphic position. sediments, derived from the adjacent horsts, were deposited.
Equivalent formations are the Semelet and Kieme formations of Analogous landscapes at the present time include the present
Cameron et al. (1980), and Bennett et al. (1981c) distinguish a rift valley province in eastern Africa, as described by Morley
marine Meujeumpo Member, consisting of limestones, calcareous (2002a), or the canyonlands of southeast Utah, as described by
sandstones and shales, defined from the Meujeumpo River. Trudgill (2002).
From the Late Cretaceous to the Early Eocene the area of the In northern Sumatra marine influences persisted, but elsewhere
Barisan Mountains formed part of a stable basement, extending the Horst and Graben Stage is represented stratigraphically by
northwards into the North Sumatra Basin and westwards into a scree, alluvial fans and fluvial sediments that pass laterally into
continental shelf in the area of the present forearc basins, with lake deposits. The sedimentation pattern was fault-controlled.
the shelf margin near the present outer arc islands. Sedimentation Alluvial fans and fluvial deposits are sedimentologically immature
on the margins of Sundaland in the Eocene, including in Sumatra, and characteristically contain clasts of granite and metamorphic