Page 104 - Sumatra Geology, Resources and Tectonic Evolution
P. 104
TERTIARY STRATIGRAPHY 91
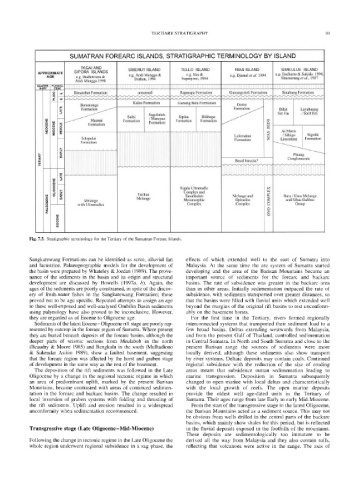
SUMATRAN FOREARC ISLANDS, STRATIGRAPHIC TERMINOLOGY BY ISLAND
PAGAI AND
APPROXIMATE SIPORA ISLANDS SIBERUT ISLAND I TELLO ISLAND NIAS ISLAND SIMEULUE ISLAND
AGE e.g. Budhitrisna & e.g. Andi Mangga & e.g. Nas & e.g. Djamal et al. 1994 e.g. Endharto & Sukido. 1994
Andi Mangga 1990 Burhan, 1994 Supanjono, 1994 Situmorang et al., 1987
CENE
i'
~
QUATER-NARY PLEISTO"' . (=' I' r i i ' ~ i = i,I i i i I' I J I~11 i , J i ! [ ~ ' ! lJj II'' 'i ~ i i I I I : ! I =! ~ j ~ . . i . I . ~ ~1 : i ' Ii II i= " !1 i i li I 'l:~
~
l
~
'
:~
i
~
d .a Simatobat Formation unnamed Raparapa Formation Gunungsitoli Formation Sinabang Formation
O
Kaleo Formation Gunung Bala Formation
Batumonga
"' aomo
Formation / Dihit Layabaung
Sagulubek Sst Fm / Sorit Fm
Saibi / Marepan Sipika Hilihego
~ Maonai Formation : Formation Formation Formation
Formation
z o ,~ - ~,~ Ai Manis
Lelematua :4 / Sibigo Sigulai
Formation Z Limestone Formation
Formation , I i i I I i
Pinang
Basal breccia? Conglomerate
2.2
m i
tll
z
8 l i Sigala Ultramafic X
Complex and
Tarikan Tanahbalah Melange and ~ Baru / Umu Melange
w Melange Melange Metamorphic Ophiolite 9 and Sibau Gabbro
o
with Ultramafics Complex Complex ~ Group
9
9
ul
LII
Fig. 7.5. Stratigraphic terminology for the Tertiary of the Sumatran Forearc Islands.
Sangkarewang Formations can be identified as scree, alluvial fan effects of which extended well to the east of Sumatra into
and lacustrine. Palaeogeographic models for the development of Malaysia. At the same time the arc system of Sumatra started
the basin were prepared by Whateley & Jordan (1989). The prove- developing and the area of the Barisan Mountains became an
nance of the sediments in the basin and its origin and structural important source of sediments for the forearc and backarc
development are discussed by Howells (1997a, b). Again, the basins. The rate of subsidence was greater in the backarc area
ages of the sediments are poorly constrained, in spite of the discov- than in other areas. Initially sedimentation outpaced the rate of
ery of fresh-water fishes in the Sangkarewang Formation; these subsidence, with sediments transported over greater distances, so
proved not to be age specific. Repeated attempts to assign an age that the basins were filled with fluvial units which extended well
to these well-exposed and well-analysed Ombilin Basin sediments beyond the margins of the original rift basins to rest unconform-
using palynology have also proved to be inconclusive. However, ably on the basement horsts.
they are regarded as of Eocene to Oligocene age. For the first time in the Tertiary, rivers formed regionally
Sediments of the latest Eocene-Oligocene rift stage are poorly rep- interconnected systems that transported their sediment load to a
resented by outcrop in the forearc region of Sumatra. Where present few broad basins. Deltas extending westwards from Malaysia,
they are buried beneath deposits of the forearc basins, although the and from the present Gulf of Thailand, controlled sedimentation
deeper parts of seismic sections from Meulaboh in the north in Central Sumatra. In North and South Sumatra and close to the
(Beaudry & Moore 1985) and Bengkulu in the south (Mulhadiono present Barisan range the sources of sediments were more
& Sukendar Asikin 1989), show a faulted basement, suggesting locally derived, although these sediments also show transport
that the forearc region was affected by the horst and graben stage by river systems. Deltaic deposits may contain coals. Continued
of development in the same way as the rest of the basement. regional subsidence with the reduction of the size of eroding
The deposition of the rift sediments was followed in the Late areas meant that subsidence outran sedimentation leading to
Oligocene by a change in the regional tectonic regime in which marine transgression. Deposition in Sumatra subsequently
an area of predominant uplift, marked by the present Barisan changed to open marine with local deltas and characteristically
Mountains, became contrasted with areas of continued sedimen- with the local growth of reefs. The open marine deposits
tation in the forearc and backarc basins. The change resulted in provide the oldest well age-dated units in the Tertiary of
local inversion of graben systems with folding and thrusting of Sumatra. Their ages range from late Early to early Mid-Miocene.
the rift sediments. Uplift and erosion resulted in a widespread From the start of the transgressive stage in the latest Oligocene,
unconformity when sedimentation recommenced. the Barisan Mountains acted as a sediment source. This may not
be obvious from wells drilled in the central parts of the backarc
basins, which mainly show shales for this period, but is reflected
Transgressive stage (Late Oligocene-Mid-Miocene) in the fluvial deposits exposed in the foothills of the mountains.
These deposits are sedimentologically too immature to be
Following the change in tectonic regime in the Late Oligocene the derived all the way fi'om Malaysia and they also contain tufts,
whole region underwent regional subsidence in a sag phase, the reflecting that volcanoes were active in the range. The axis of