Page 44 - Sumatra Geology, Resources and Tectonic Evolution
P. 44
PRE-TERTIARY STRATIGRAPHY 3 !
I I I
102~ 30' 45' 103*00'
Formation; TIGAPULUH
MOUNTAINS
45' 45'
--I ,"Ut/l l 1
Inliers of
Gangsal Triassic-Jurassic
Formation Granites
in Limau I- TIGAPULUH GROUP
Condong (volcanic) Member
~'~ Mentulu Formation
ld~:':~?:4 (pebbly mudstones)
[:~i::i::iiiii::i! t Pengabuhan Formation
~.,x,%..~
[~}x...'..s ] Gangsal Formation
1 ooo's : Gangsal
:Formation
.'.-.-\'.-.--.-.-...N~...2I~Mentulu
.~.N[," [ "15engabuhan ~ _.,-, %;
~
....
~,'-.'.:,~
~\... :. :...........-7. ---.
0 5 10 15 20kin
15' L to Jambi
15' 30' lO3~OO '
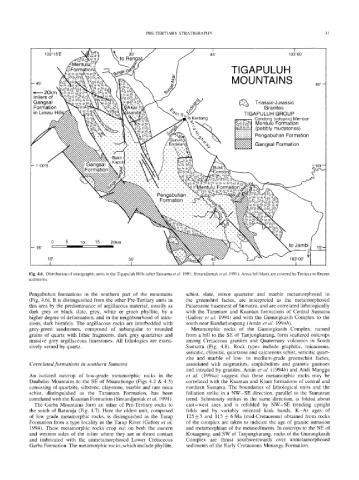
Fig. 4.6. Distribution of stratigraphic units in the Tigapuluh Hills (alter Suwama et al. 1991" Simandjuntak et al. 1991 ). Areas left blank are covered by Tertiary to Recent
sediments.
Pengabuhan formations in the southern part of the mountains schist, slate, minor quartzite and marble metamorphosed in
(Fig. 4.6). It is distinguished from the other Pre-Tertiary units in the greenshist facies, are interpreted as the metamorphosed
this area by the predominance of argillacous material, usually as Palaeozoic basement of Sumatra, and are correlated lithologically
dark grey or black slate, grey, white or green phyllite, by a with the Tarantam and Kuantan formations of Central Sumatra
higher degree of deformation, and in the neighbourhood of intru- (Gafoer et al. 1994) and with the Gunungkasih Complex to the
sions, dark hornfels. The argillacous rocks are interbedded with south near Bandarlampung (Amin et al. 1994b).
grey-green sandstones, composed of subangular to rounded Metamorphic rocks of the Gunungkasih Complex, named
grains of quartz with lithic fragments, dark grey quartzites and from a hill to the SE of Tanjungkarang, form scattered outcrops
massive grey argillaceous limestones. All lithologies are exten- among Cretaceous granites and Quaternary volcanics in South
sively veined by quartz. Sumatra (Fig. 4.8). Rock types include graphitic, micaceous,
sericitic, chloritic, quartzose and calcareous schist, sericitic quart-
zite and marble of low- to medium-grade greenschist facies,
Correlated ormations in southern Sumatra associated with migmatites, amphibolites and granitic gneisses
f
and intruded by granites. Amin et al. (1994b) and Andi Mangga
An isolated outcrop of low-grade metamorphic rocks in the et al. (1994a) suggest that these metamorphic rocks may be
Duabelas Mountains to the SE of Muarabungo (Figs 4.2 & 4.5) correlated with the Kuantan and Kluet formations of central and
consisting of quartzite, siltstone, claystone, marble and rare mica northern Sumatra. The boundaries of lithological units and the
schist, distinguished as the Tarantam Formation, has been foliation strike in a NW-SE direction, parallel to the Sumatran
correlated with the Kuantan Formation (Simandjuntak et al. 1991). trend. Schistosity strikes in the same direction, is folded about
The Garba Mountains form an inlier of Pre-Tertiary rocks to east-west axes and is refolded by NW-SE trending upright
the south of Baturaja (Fig. 4.7). Here the oldest unit, composed folds and by variably oriented kink bands. K-Ar ages of
of low grade metamorphic rocks, is distinguished as the Tarap 125 +5 and 115 __ 6 Ma (mid-Cretaceous) obtained from rocks
Formation from a type locality in the Tarap River (Gafoer et al. of the complex are taken to indicate the age of granite intrusion
1994). These metamorphic rocks crop out on both the eastern and metamorphism of the metasediments. In outcrops to the NE of
and western sides of the inlier where they are in thrust contact Kotaagung, and SW of Tanjungkarang, rocks of the Gunungkasih
and imbricated with the unmetamorphosed Lower Cretaceous Complex are thrust southwestwards over unmetamorphosed
Garba Formation. The metamorphic rocks, which include phyllite, sediments of the Early Cretaceous Menanga Formation.