Page 137 - Sustainable Cities and Communities Design Handbook
P. 137
114 Sustainable Cities and Communities Design Handbook
wind energy that are complementary and may be quite manageable for inte-
gration into a grid system (Abbess, 2009; Clark, 2012; Jin, 2010).
What is a solar electricity system? A solar electricity system is a system for
utilizing abundant sun’s energy to produce electricity or heat for consumers.
For example, the solar PV cell is a physical device that converts light into
electricity. Fig. 6.2 is a schematic to illustrate the physical mechanism of a
solar PV cell in producing solar electricity. Solar electricity industry is
composed of many types of competing technologies with various cost struc-
ture, efficiency, and scalability factors that are important to the renewable
energy industry sector.
The availability and future prospects are very promising at this time for the
following three solar technologies: (1) solar thermal power, (2) solar PV
panels, and (3) solar heaters. For example, the utility-scale solar thermal power
plants (STPP) have been constructed rapidly in the last two decades. More-
over, the solar PV panels offer scalable power that has been installed today on
thousands of rooftops in California.
The solar PV systems, which are made up of individual solar cells, are
becoming more affordable and reliable all the time. The solar PV panels are
made modular, scalable, and suitable for distributed generation. Moreover, the
scalable solar panels can be utilized for utility-scale power plants.
There are several types of devices that may be required to connect solar PV
systems to be suitable for individual consumer energy use and/or for supplying
power to the electric grid. The most important unit is the inverter. The inverter
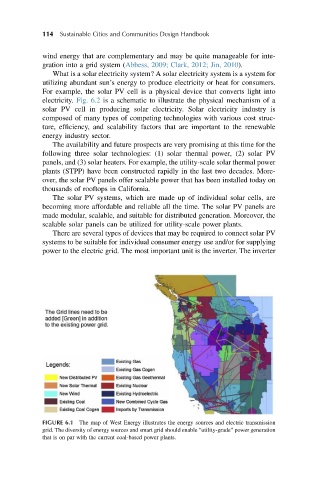
FIGURE 6.1 The map of West Energy illustrates the energy sources and electric transmission
grid. The diversity of energy sources and smart grid should enable “utility-grade” power generation
that is on par with the current coal-based power plants.