Page 152 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 152
Ch004-P373623.qxd 3/26/07 4:46 PM Page 131
Sustainable Development and Environmental Reform
Continual improvement 131
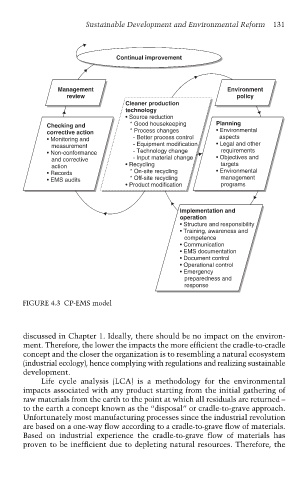
Management Environment
review policy
Cleaner production
technology
• Source reduction
Checking and * Good housekeeping Planning
corrective action * Process changes • Environmental
• Monitoring and - Better process control aspects
measurement - Equipment modification • Legal and other
• Non-conformance - Technology change requirements
and corrective - Input material change • Objectives and
action • Recycling targets
• Records * On-site recycling • Environmental
• EMS audits * Off-site recycling management
• Product modification programs
Implementation and
operation
• Structure and responsibility
• Training, awareness and
competence
• Communication
• EMS documentation
• Document control
• Operational control
• Emergency
preparedness and
response
FIGURE 4.3 CP-EMS model
discussed in Chapter 1. Ideally, there should be no impact on the environ-
ment. Therefore, the lower the impacts the more efficient the cradle-to-cradle
concept and the closer the organization is to resembling a natural ecosystem
(industrial ecology), hence complying with regulations and realizing sustainable
development.
Life cycle analysis (LCA) is a methodology for the environmental
impacts associated with any product starting from the initial gathering of
raw materials from the earth to the point at which all residuals are returned –
to the earth a concept known as the “disposal” or cradle-to-grave approach.
Unfortunately most manufacturing processes since the industrial revolution
are based on a one-way flow according to a cradle-to-grave flow of materials.
Based on industrial experience the cradle-to-grave flow of materials has
proven to be inefficient due to depleting natural resources. Therefore, the