Page 60 - Sustainable On-Site CHP Systems Design, Construction, and Operations
P. 60
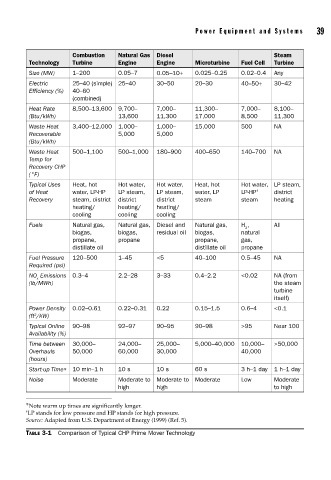
Power Equipment and Systems 39
Combustion Natural Gas Diesel Steam
Technology Turbine Engine Engine Microturbine Fuel Cell Turbine
Size (MW) 1–200 0.05–7 0.05–10+ 0.025–0.25 0.02–0.4 Any
Electric 25–40 (simple) 25–40 30–50 20–30 40–50+ 30–42
Efficiency (%) 40–60
(combined)
Heat Rate 8,500–13,600 9,700– 7,000– 11,300– 7,000– 8,100–
(Btu/kWh) 13,600 11,300 17,000 8,500 11,300
Waste Heat 3,400–12,000 1,000– 1,000– 15,000 500 NA
Recoverable 5,000 5,000
(Btu/kWh)
Waste Heat 500–1,100 500–1,000 180–900 400–650 140–700 NA
Temp for
Recovery CHP
(°F)
Typical Uses Heat, hot Hot water, Hot water, Heat, hot Hot water, LP steam,
of Heat water, LP-HP LP steam, LP steam, water, LP LP-HP † district
Recovery steam, district district district steam steam heating
heating/ heating/ heating/
cooling cooling cooling
Fuels Natural gas, Natural gas, Diesel and Natural gas, H , All
2
biogas, biogas, residual oil biogas, natural
propane, propane propane, gas,
distillate oil distillate oil propane
Fuel Pressure 120–500 1–45 <5 40–100 0.5–45 NA
Required (psi)
NO Emissions 0.3–4 2.2–28 3–33 0.4–2.2 <0.02 NA (from
x
(lb/MWh) the steam
turbine
itself)
Power Density 0.02–0.61 0.22–0.31 0.22 0.15–1.5 0.6–4 <0.1
2
(ft /kW)
Typical Online 90–98 92–97 90–95 90–98 >95 Near 100
Availability (%)
Time between 30,000– 24,000– 25,000– 5,000–40,000 10,000– >50,000
Overhauls 50,000 60,000 30,000 40,000
(hours)
Start-up Time∗ 10 min–1 h 10 s 10 s 60 s 3 h–1 day 1 h–1 day
Noise Moderate Moderate to Moderate to Moderate Low Moderate
high high to high
∗ Note warm up times are significantly longer.
† LP stands for low pressure and HP stands for high pressure.
Source: Adapted from U.S. Department of Energy (1999) (Ref. 5).
TABLE 3-1 Comparison of Typical CHP Prime Mover Technology