Page 189 -
P. 189
174 BARBER AND GRASER
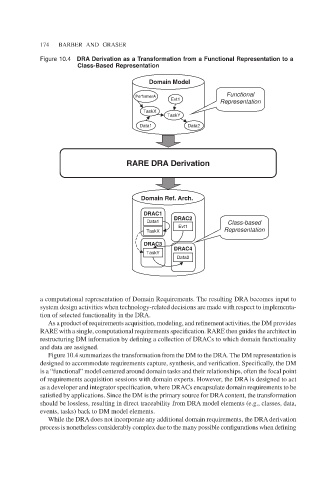
Figure 10.4 DRA Derivation as a Transformation from a Functional Representation to a
Class-Based Representation
Domain Model
Functional
PerformerA
Evt1 Representation
TaskX
TaskY
Data1 Data2
RARE DRA Derivation
Domain Ref. Arch.
DRAC1
DRAC2
Data1 Class-based
Evt1
TaskX Representation
DRAC3
DRAC4
TaskY
Data2
a computational representation of Domain Requirements. The resulting DRA becomes input to
system design activities when technology-related decisions are made with respect to implementa-
tion of selected functionality in the DRA.
As a product of requirements acquisition, modeling, and refinement activities, the DM provides
RARE with a single, computational requirements specification. RARE then guides the architect in
restructuring DM information by defining a collection of DRACs to which domain functionality
and data are assigned.
Figure 10.4 summarizes the transformation from the DM to the DRA. The DM representation is
designed to accommodate requirements capture, synthesis, and verification. Specifically, the DM
is a “functional” model centered around domain tasks and their relationships, often the focal point
of requirements acquisition sessions with domain experts. However, the DRA is designed to act
as a developer and integrator specification, where DRACs encapsulate domain requirements to be
satisfied by applications. Since the DM is the primary source for DRA content, the transformation
should be lossless, resulting in direct traceability from DRA model elements (e.g., classes, data,
events, tasks) back to DM model elements.
While the DRA does not incorporate any additional domain requirements, the DRA derivation
process is nonetheless considerably complex due to the many possible configurations when defining