Page 91 -
P. 91
58 Part 1 • SyStemS analySiS FundamentalS
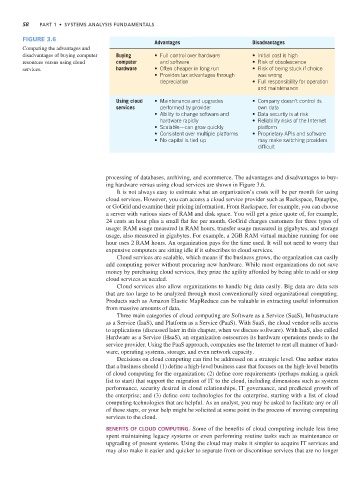
Figure 3.6
Advantages Disadvantages
Comparing the advantages and
disadvantages of buying computer Buying • Full control over hardware • Initial cost is high
resources versus using cloud computer and software • Risk of obsolescence
services. hardware • Often cheaper in long run • Risk of being stuck if choice
• Provides tax advantages through was wrong
depreciation • Full responsibility for operation
and maintenance
Using cloud • Maintenance and upgrades • Company doesn’t control its
services performed by provider own data
• Ability to change software and • Data security is at risk
hardware rapidly • Reliability risks of the Internet
• Scalable—can grow quickly platform
• Consistent over multiple platforms • Proprietary APIs and software
• No capital is tied up may make switching providers
difficult
processing of databases, archiving, and ecommerce. The advantages and disadvantages to buy-
ing hardware versus using cloud services are shown in Figure 3.6.
It is not always easy to estimate what an organization’s costs will be per month for using
cloud services. However, you can access a cloud service provider such as Rackspace, Datapipe,
or GoGrid and examine their pricing information. From Rackspace, for example, you can choose
a server with various sizes of RAM and disk space. You will get a price quote of, for example,
24 cents an hour plus a small flat fee per month. GoGrid charges customers for three types of
usage: RAM usage measured in RAM hours, transfer usage measured in gigabytes, and storage
usage, also measured in gigabytes. For example, a 2GB RAM virtual machine running for one
hour uses 2 RAM hours. An organization pays for the time used. It will not need to worry that
expensive computers are sitting idle if it subscribes to cloud services.
Cloud services are scalable, which means if the business grows, the organization can easily
add computing power without procuring new hardware. While most organizations do not save
money by purchasing cloud services, they prize the agility afforded by being able to add or stop
cloud services as needed.
Cloud services also allow organizations to handle big data easily. Big data are data sets
that are too large to be analyzed through most conventionally sized organizational computing.
Products such as Amazon Elastic MapReduce can be valuable in extracting useful information
from massive amounts of data.
Three main categories of cloud computing are Software as a Service (SaaS), Infrastructure
as a Service (IaaS), and Platform as a Service (PaaS). With SaaS, the cloud vendor sells access
to applications (discussed later in this chapter, when we discuss software). With IaaS, also called
Hardware as a Service (HaaS), an organization outsources its hardware operations needs to the
service provider. Using the PaaS approach, companies use the Internet to rent all manner of hard-
ware, operating systems, storage, and even network capacity.
Decisions on cloud computing can first be addressed on a strategic level. One author states
that a business should (1) define a high-level business case that focuses on the high-level benefits
of cloud computing for the organization; (2) define core requirements (perhaps making a quick
list to start) that support the migration of IT to the cloud, including dimensions such as system
performance, security desired in cloud relationships, IT governance, and predicted growth of
the enterprise; and (3) define core technologies for the enterprise, starting with a list of cloud
computing technologies that are helpful. As an analyst, you may be asked to facilitate any or all
of these steps, or your help might be solicited at some point in the process of moving computing
services to the cloud.
BENEFITS OF CLOUD COMPUTING. Some of the benefits of cloud computing include less time
spent maintaining legacy systems or even performing routine tasks such as maintenance or
upgrading of present systems. Using the cloud may make it simpler to acquire IT services and
may also make it easier and quicker to separate from or discontinue services that are no longer