Page 30 - Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics
P. 30
10 Basic physical concepts
A compound is different than a simple mixture of elements. If hydrogen and oxy-
gen are mixed, the result is a colorless, odorless gas, just like either element is a gas
separately. A spark, however, will cause the molecules to join together; this will liber-
ate energy in the form of light and heat. Under the right conditions, there will be a vi-
olent explosion, because the two elements join eagerly. Water is chemically illustrated
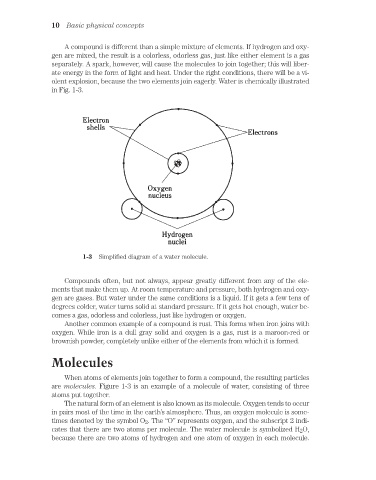
in Fig. 1-3.
1-3 Simplified diagram of a water molecule.
Compounds often, but not always, appear greatly different from any of the ele-
ments that make them up. At room temperature and pressure, both hydrogen and oxy-
gen are gases. But water under the same conditions is a liquid. If it gets a few tens of
degrees colder, water turns solid at standard pressure. If it gets hot enough, water be-
comes a gas, odorless and colorless, just like hydrogen or oxygen.
Another common example of a compound is rust. This forms when iron joins with
oxygen. While iron is a dull gray solid and oxygen is a gas, rust is a maroon-red or
brownish powder, completely unlike either of the elements from which it is formed.
Molecules
When atoms of elements join together to form a compound, the resulting particles
are molecules. Figure 1-3 is an example of a molecule of water, consisting of three
atoms put together.
The natural form of an element is also known as its molecule. Oxygen tends to occur
in pairs most of the time in the earth’s atmosphere. Thus, an oxygen molecule is some-
times denoted by the symbol O 2 . The “O” represents oxygen, and the subscript 2 indi-
cates that there are two atoms per molecule. The water molecule is symbolized H 2 O,
because there are two atoms of hydrogen and one atom of oxygen in each molecule.