Page 139 - The Biochemistry of Inorganic Polyphosphates
P. 139
Char Count= 0
15:39
March 9, 2004
WU095/Kulaev
WU095-07
The functions of polyphosphates in higher eukaryotes 123
Bone tissues
Blood plasma
Participation in the
Antibacterial and Other tissues osteoblasts’
antiviral action differentiation and
mineralization
Lysosomes and
Cell nucleus
Membranes secretory vesicles
Gene activity regulation
PolyP/PHB Sequestration of cations
complexes, and bioactive amines
transport
processes
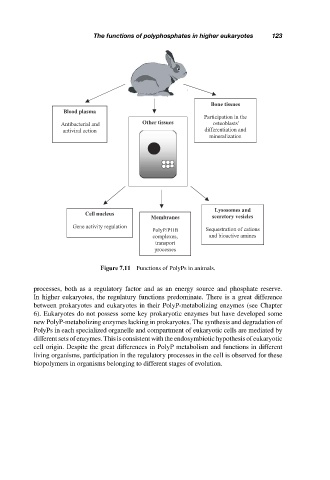
Figure 7.11 Functions of PolyPs in animals.
processes, both as a regulatory factor and as an energy source and phosphate reserve.
In higher eukaryotes, the regulatury functions predominate. There is a great difference
between prokaryotes and eukaryotes in their PolyP-metabolizing enzymes (see Chapter
6). Eukaryotes do not possess some key prokaryotic enzymes but have developed some
new PolyP-metabolizing enzymes lacking in prokaryotes. The synthesis and degradation of
PolyPs in each specialized organelle and compartment of eukaryotic cells are mediated by
different sets of enzymes. This is consistent with the endosymbiotic hypothesis of eukaryotic
cell origin. Despite the great differences in PolyP metabolism and functions in different
living organisms, participation in the regulatory processes in the cell is observed for these
biopolymers in organisms belonging to different stages of evolution.