Page 267 - Bruce Ellig - The Complete Guide to Executive Compensation (2007)
P. 267
Chapter 6. Employee Benefits and Perquisites 253
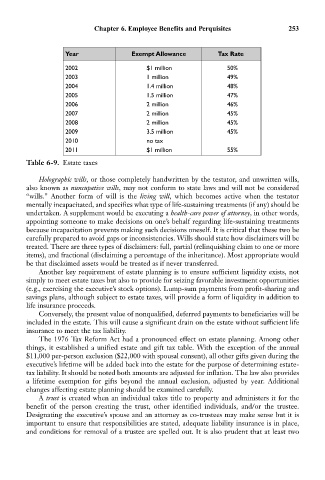
Year Exempt Allowance Tax Rate
2002 $1 million 50%
2003 1 million 49%
2004 1.4 million 48%
2005 1.5 million 47%
2006 2 million 46%
2007 2 million 45%
2008 2 million 45%
2009 3.5 million 45%
2010 no tax
2011 $1 million 55%
Table 6-9. Estate taxes
Holographic wills, or those completely handwritten by the testator, and unwritten wills,
also known as nuncupative wills, may not conform to state laws and will not be considered
“wills.” Another form of will is the living will, which becomes active when the testator
mentally incapacitated, and specifies what type of life-sustaining treatments (if any) should be
undertaken. A supplement would be executing a health-care power of attorney, in other words,
appointing someone to make decisions on one’s behalf regarding life-sustaining treatments
because incapacitation prevents making such decisions oneself. It is critical that these two be
carefully prepared to avoid gaps or inconsistencies. Wills should state how disclaimers will be
treated. There are three types of disclaimers: full, partial (relinquishing claim to one or more
items), and fractional (disclaiming a percentage of the inheritance). Most appropriate would
be that disclaimed assets would be treated as if never transferred.
Another key requirement of estate planning is to ensure sufficient liquidity exists, not
simply to meet estate taxes but also to provide for seizing favorable investment opportunities
(e.g., exercising the executive’s stock options). Lump-sum payments from profit-sharing and
savings plans, although subject to estate taxes, will provide a form of liquidity in addition to
life insurance proceeds.
Conversely, the present value of nonqualified, deferred payments to beneficiaries will be
included in the estate. This will cause a significant drain on the estate without sufficient life
insurance to meet the tax liability.
The 1976 Tax Reform Act had a pronounced effect on estate planning. Among other
things, it established a unified estate and gift tax table. With the exception of the annual
$11,000 per-person exclusion ($22,000 with spousal consent), all other gifts given during the
executive’s lifetime will be added back into the estate for the purpose of determining estate-
tax liability. It should be noted both amounts are adjusted for inflation. The law also provides
a lifetime exemption for gifts beyond the annual exclusion, adjusted by year. Additional
changes affecting estate planning should be examined carefully.
A trust is created when an individual takes title to property and administers it for the
benefit of the person creating the trust, other identified individuals, and/or the trustee.
Designating the executive’s spouse and an attorney as co-trustees may make sense but it is
important to ensure that responsibilities are stated, adequate liability insurance is in place,
and conditions for removal of a trustee are spelled out. It is also prudent that at least two