Page 486 - Bruce Ellig - The Complete Guide to Executive Compensation (2007)
P. 486
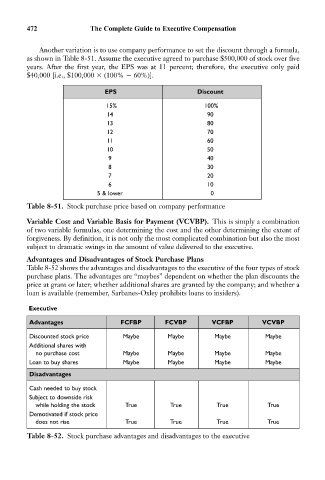
472 The Complete Guide to Executive Compensation
Another variation is to use company performance to set the discount through a formula,
as shown in Table 8-51. Assume the executive agreed to purchase $500,000 of stock over five
years. After the first year, the EPS was at 11 percent; therefore, the executive only paid
$40,000 [i.e., $100,000 (100% 60%)].
EPS Discount
15% 100%
14 90
13 80
12 70
11 60
10 50
9 40
8 30
7 20
6 10
5 & lower 0
Table 8-51. Stock purchase price based on company performance
Variable Cost and Variable Basis for Payment (VCVBP). This is simply a combination
of two variable formulas, one determining the cost and the other determining the extent of
forgiveness. By definition, it is not only the most complicated combination but also the most
subject to dramatic swings in the amount of value delivered to the executive.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Stock Purchase Plans
Table 8-52 shows the advantages and disadvantages to the executive of the four types of stock
purchase plans. The advantages are “maybes” dependent on whether the plan discounts the
price at grant or later; whether additional shares are granted by the company; and whether a
loan is available (remember, Sarbanes-Oxley prohibits loans to insiders).
Executive
Advantages FCFBP FCVBP VCFBP VCVBP
Discounted stock price Maybe Maybe Maybe Maybe
Additional shares with
no purchase cost Maybe Maybe Maybe Maybe
Loan to buy shares Maybe Maybe Maybe Maybe
Disadvantages
Cash needed to buy stock
Subject to downside risk
while holding the stock True True True True
Demotivated if stock price
does not rise True True True True
Table 8-52. Stock purchase advantages and disadvantages to the executive